A) back down the Phillips curve toward an unemployment rate that is closer to the natural rate of unemployment.
B) up the Phillips curve toward an unemployment rate that is closer to the natural rate of unemployment.
C) back down the Phillips curve toward an unemployment rate that is further from the natural rate of unemployment.
D) up the Phillips curve toward an unemployment rate that is further from the natural rate of unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prior to the 1970s, the model of choice was the aggregate expenditures model. According to This model, if the economy was in equilibrium at an income greater than the full employment level, then the primary economic problem would be
A) excessive bank lending.
B) potential crises in financial markets.
C) inflation.
D) excess aggregate demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A Phillips phase emerges because wages are flexible and adjust more quickly than anticipated.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following statement: "President Carter expressed concern about reports of rising inflation but insisted the economy is on the right course. He pointed to recent reductions in unemployment as evidence that his economic policies are working." Identify the stage of the inflation-unemployment relationship.
A) The stagflation phase
B) The recovery phase
C) The Phillips phase
D) The contraction phase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the efficiency wage theory holds,
A) wage rigidity that perpetuates a recessionary gap is transformed from a temporary phenomenon to a permanent feature.
B) self-correction will automatically eliminate a recessionary gap.
C) increases in real wages will be required to eliminate a recessionary gap.
D) increases in nominal wages will be required to close a recessionary gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the full-employment level of real GDP is increasing at a rate of 3% per period and the money supply is growing at a 3% rate. Using the equation of exchange, what is the value of the long-run inflation rate, assuming constant velocity?
A) 6%
B) 3%
C) 1%
D) 0%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In general, the duration of job search will be shorter if
A) less job-market information is available.
B) it is more costly to obtain job-search information.
C) there are fewer employment agencies.
D) unemployment compensation benefits decrease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prior to the 1970s, the model of choice was the aggregate expenditures model. According to This model, if the economy was in equilibrium below full employment, then the primary economic problem would be
A) unemployment.
B) deflation.
C) financing the government budget deficit.
D) financing unemployment compensation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stagflation implies that
A) policymakers can choose to have less unemployment if they are willing to accept a higher rate of inflation.
B) a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment may not always exist.
C) any relationship between the inflation and unemployment was purely random.
D) the relationship predicted by the Phillips curve is stable.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16-1 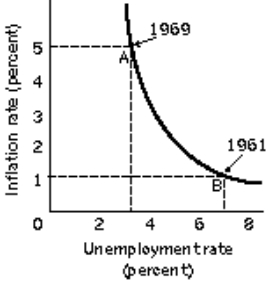 -Refer to Figure 16-1. Consider point A where inflation is relatively high and unemployment is relatively low. In order to move down the curve toward point B, what fiscal policy measures should the policymakers undertake?
-Refer to Figure 16-1. Consider point A where inflation is relatively high and unemployment is relatively low. In order to move down the curve toward point B, what fiscal policy measures should the policymakers undertake?
A) Decrease taxes and government spending
B) Increase taxes and government spending
C) Increase taxes and decrease government spending
D) Decrease taxes and increase government spending
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16-7 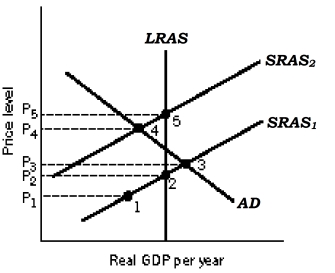 -Refer to Figure 16-7. If the economy is at point 4, boosting aggregate demand through
Expansionary policies will most likely lead to
-Refer to Figure 16-7. If the economy is at point 4, boosting aggregate demand through
Expansionary policies will most likely lead to
A) a stagflation phase.
B) a recovery phase.
C) a Phillips phase.
D) a contraction phase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Sustained inflation over many years is most likely due to increases in the money supply in excess of increases in potential output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a cost of unemployment? I. output foregone II. unemployment compensation that must be paid III. rising inflation that erodes the value of money
A) I, II, and III
B) I and II
C) I and III
D) II and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a recovery phase,
A) inflation and unemployment both increase.
B) inflation and unemployment stay the same.
C) inflation and unemployment both decrease.
D) unemployment decreases and inflation increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The essential feature of a stagflation phase is
A) a shift in the short run aggregate supply curve to the right.
B) changes in expectations about the price level.
C) falling unemployment and rising inflation.
D) a shift of the LRAS curve to the right.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16-3
Panel (a) Panel (b) 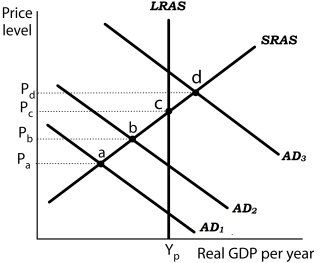
 Suppose the level of potential output (YP) is $1,000 billion and the natural rate of unemployment is 5%. In Panel (a) , the aggregate demand curve in Period 1 is AD1. Assume that the price level in Period 1 has risen by 1.5% from the previous period and the unemployment rate is 10%. Thus, in Panel (b) point F shows an initial rate of inflation of 1.5% and an unemployment rate of 10%. Similarly, point b in Panel (a) corresponds to point G in Panel (b) and point d in Panel (a) corresponds to point H in Panel (b) .
-Refer to Figure 16-3. Suppose the economy is operating at point a. If policymakers
Undertake expansionary policies in period 1, what happens if there are lags in the application
Of policy?
Suppose the level of potential output (YP) is $1,000 billion and the natural rate of unemployment is 5%. In Panel (a) , the aggregate demand curve in Period 1 is AD1. Assume that the price level in Period 1 has risen by 1.5% from the previous period and the unemployment rate is 10%. Thus, in Panel (b) point F shows an initial rate of inflation of 1.5% and an unemployment rate of 10%. Similarly, point b in Panel (a) corresponds to point G in Panel (b) and point d in Panel (a) corresponds to point H in Panel (b) .
-Refer to Figure 16-3. Suppose the economy is operating at point a. If policymakers
Undertake expansionary policies in period 1, what happens if there are lags in the application
Of policy?
A) The economy may not experience any change in the price level or level of employment.
B) The economy could move past full employment to AD3 and encounter an inflationary gap.
C) The economy could be stuck in a below full-employment equilibrium such as at point b.
D) The economy could experience deflation resulting in a movement along the Phillips phase from point G to point F.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a recovery phase,
A) inflation and unemployment fall.
B) inflation rises as unemployment falls.
C) inflation falls as unemployment rises.
D) inflation and real GDP rise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long-run, only a change in the _______ is likely to affect the inflation rate associated With a particular rate of growth in the money supply.
A) aggregate demand
B) short-run aggregate supply
C) rate of economic growth
D) expectations about the price level
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The short-run Phillips curve implies a positive relationship between inflation and unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Structural unemployment is best reduced by
A) job training programs to retool workers with new skills.
B) improved job-market information.
C) an increasing unemployment compensation benefits.
D) offering above equilibrium wages to attract workers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 138
Related Exams