A) Monitor for sudden onset of ventricular tachycardia.
B) Perform neurologic checks every 4 hours.
C) Monitor for deterioration to third-degree block.
D) Assess skin turgor for dehydration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient with atrial fibrillation is scheduled for elective cardioversion. What teaching should the nurse prepare for this patient?
A) Short-term use of beta blockers
B) Short-term use of anticoagulant therapy
C) Long-term use of calcium channel blockers
D) Long-term use of antiarrhythmic medication
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse is interpreting an ECG strip. What would describe paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) ? Select all that apply.
A) QRS width is 0.18 second.
B) Heart rate is between 150 and 250 beats per minute.
C) The P wave is hidden in the preceding T wave; therefore, the PR interval cannot be measured.
D) The increased rate can start abruptly and cease quickly when viewing a cardiac monitor to validate its presence.
E) It is treated with carotid massage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient with sick sinus syndrome loses consciousness for 15 seconds during periods of asystole. What should the nurse expect to be prescribed for this patient?
A) Atropine
B) Stress reduction
C) Carotid massage
D) Permanent pacemaker
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse reviews synchronized cardioversion with a new graduate. What should the nurse include when reviewing this procedure? Select all that apply.
A) The shock is synchronized with the QRS complex.
B) The shock will occur on the R wave.
C) A sedative will be provided before the procedure.
D) Pain medication will be provided before the procedure.
E) The shock will occur on the T wave.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When evaluating the health history of a patient with complete heart block, what should the nurse identify as potential causes for this health problem? Select all that apply.
A) Myocarditis
B) Degenerative heart disease
C) Severe aortic stenosis
D) Digitalis toxicity
E) Currently being treated for acute myocardial infarction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient is demonstrating second-degree heart block (Wenckebach [type I]) . What characteristic of this rhythm should the nurse recognize?
A) Progressive lengthening of the PR interval until a QRS is dropped
B) Prolonged PR interval greater than 0.22
C) Complete disassociation of the atria and ventricles
D) Consistent PR interval with occasional dropped QRS complexes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
CPR is started on a patient who has developed ventricular fibrillation. The patient is defibrillated once with the resulting rhythm. Which intervention should the nurse implement next? 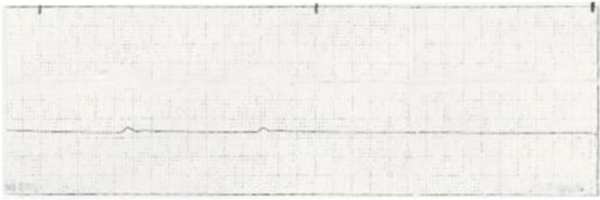
A) Defibrillate the patient with 360 joules.
B) Administer atropine 1 mg IV push and repeat every 3 minutes.
C) Infuse amiodarone 300 mg IV push slowly.
D) Administer epinephrine 1 mg IV push.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient in the emergency department is in supraventricular tachycardia. Which actions should be taken for this patient? Select all that apply.
A) Start CPR and defibrillate at 200 joules.
B) Start oxygen at 2 L/min via nasal cannula.
C) Give atropine 1 mg IVP.
D) Give epinephrine 1 mg IVP.
E) Give adenosine 6 mg IVP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient receiving procainamide develops pulseless ventricular tachycardia. What should the nurse expect to be done for this patient?
A) Unsynchronized shock
B) Synchronized cardioversion
C) Temporary pacemaker insertion
D) Insertion of a permanent pacemaker
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient is experiencing chest pain, shortness of breath, and lethargy. The patient's vital signs are BP 88/58, HR 40, RR 20. Which nursing action is a priority for this patient?
A) Nitroglycerin 1 tablet sublingual
B) Aspirin 325 mg PO
C) Morphine 2 mg IVP
D) Atropine 1 mg IVP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient is placed on continuous cardiac monitoring. What should the nurse realize is occurring when the rhythm displays a flat, isoelectric line?
A) Polarization
B) Depolarization
C) Repolarization
D) Absolute refractory period
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What best describes the ECG rhythm of atrial fibrillation?
A) No P wave but waves that can be described similar to a picket fence or sawtooth pattern that are regularly spaced between normal QRS waves
B) No consistent P waves, only an erratic and wavy baseline between normally configured QRS waves
C) A progressive deterioration of the wavy baseline with irregular R to R spacing that leads to ventricular tachycardia and a cardiac arrest situation
D) A QRS width greater than 0.12 second and lasting about 30 seconds before ventricular fibrillation occurs
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse reviews a patient's prescribed scheduled and PRN medications. Which medication affects cardiac contractility? Select all that apply.
A) Digoxin
B) Dopamine
C) Epinephrine
D) Morphine
E) Atropine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse reviews the characteristics of a normal QRS complex on a patient's cardiac rhythm strip. What should the nurse identify as characteristics of this complex? Select all that apply.
A) The first downward deflection after the P wave is the Q wave.
B) The first upward deflection after the P wave is the R wave.
C) The first downward deflection after the R wave is the S wave.
D) It usually measures less than 0.12 seconds or less than 3 small boxes.
E) It ends at the beginning of the T wave.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient has the following rhythm on the monitor. The patient is alert and oriented and denies any complaints at present. What should the nurse do first? 
A) Administer a precordial thump.
B) Check lead placement on the patient.
C) Begin CPR and call for a defibrillator.
D) Administer epinephrine 1 mg IV every 3 minutes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order to correctly manage ventricular dysrhythmias, the nurse should expect to implement which treatment?
A) Magnesium to terminate ventricular tachycardia pattern called torsades de pointes that was noted on the ECG strip
B) Potassium chloride (KCl) replacement for a potassium level of 4 mEq/mL
C) Procainamide for developing coarse ventricular fibrillation
D) Synchronized cardioversion after atropine is given for ventricular tachycardia
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient is scheduled for surgery to implant a cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) . What should the nurse expect to see documented in the patient's medical record?
A) Documented episodes of bigeminy
B) Permanent pacemaker failing to pace
C) History of episodes of ventricular fibrillation
D) Malfunctioning lead on an external temporary pacemaker
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ECG strip of a patient with a transvenous ventricular demand pacemaker shows QRS complexes without pacer spikes. What should the nurse do?
A) Plan for immediate removal of pacer lead wires.
B) Continue to observe the patient and the ECG rhythm.
C) Call the health care provider and explain that capture has been lost.
D) Call a code for ventricular fibrillation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 39 of 39
Related Exams