A) prepare to place the patient on a transcutaneous pacemaker.
B) give the patient atropine to shorten the PR interval.
C) monitor the rhythm and patient's condition.
D) give the patient an antiarrhythmic medication.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The patient is admitted with sinus pauses causing periods of loss of consciousness.The patient is asymptomatic,awake and alert,but fatigued.He solve questions appropriately.When admitting this patient,the nurse should first
A) prepare the patient for temporary pacemaker insertion.
B) prepare the patient for permanent pacemaker insertion.
C) assess the patient's medication profile.
D) apply transcutaneous pacemaker paddles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm:
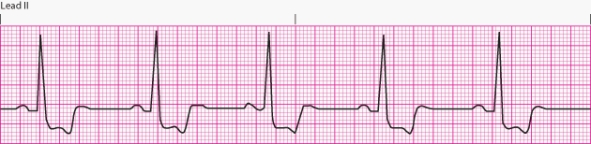
A) Normal sinus rhythm
B) Sinus bradycardia
C) Sinus tachycardia
D) Sinus arrhythmia
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse notices sinus bradycardia on the patient's cardiac monitor.The nurse should
A) give atropine to increase heart rate.
B) begin transcutaneous pacing of the patient.
C) start a dopamine infusion to stimulate heart function.
D) assess for hemodynamic instability.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm:
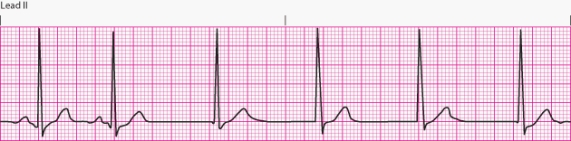
A) Junctional rhythm
B) An accelerated junctional rhythm
C) A junctional tachycardia
D) Atrial fibrillation
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse understands that in a third-degree AV block
A) every P wave is conducted to the ventricles.
B) some P waves are conducted to the ventricles.
C) none of the P waves are conducted to the ventricles.
D) the PR interval is prolonged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm:
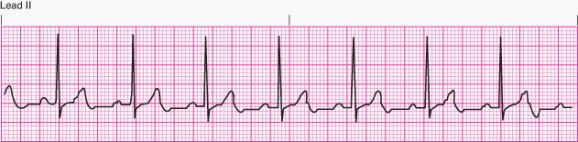
A) Normal sinus rhythm
B) Sinus bradycardia
C) Sinus tachycardia
D) Sinus arrhythmia
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about a patient diagnosed with sinus arrhythmia?
A) The heart rate varies, dependent on vagal tone and respiratory pattern.
B) Immediate treatment is essential to prevent death.
C) Sinus arrhythmia is not well tolerated by most patients.
D) PR and QRS interval measurements are prolonged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm:
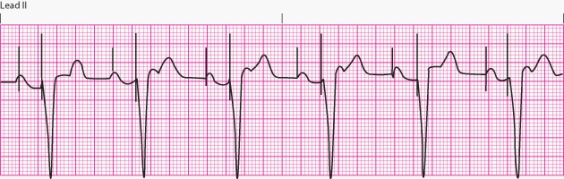
A) Atrial pacing
B) Ventricular pacing
C) Dual-chamber pacing
D) Transcutaneous pacing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm:
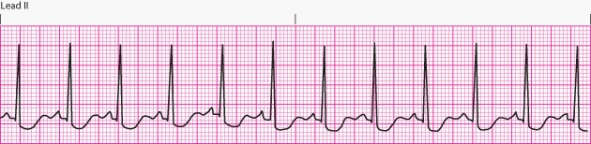
A) Normal sinus rhythm
B) Sinus bradycardia
C) Sinus tachycardia
D) Sinus arrhythmia
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm:
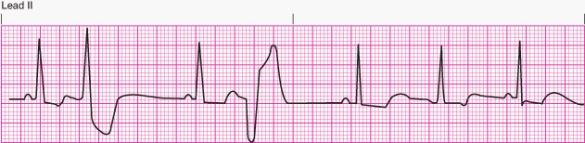
A) Sinus rhythm with multifocal premature ventricular contractions
B) Sinus rhythm with unifocal premature ventricular contractions
C) Sinus rhythm with bigeminal premature ventricular contractions
D) Sinus rhythm with paired premature ventricular contractions (couplets)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The patient is in third-degree heart block (complete heart block) and is symptomatic.The treatment for this patient is which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
A) Transcutaneous pacemaker
B) Atropine IV
C) Temporary transvenous pacemaker
D) Permanent pacemaker
E) Amiodarone IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm:
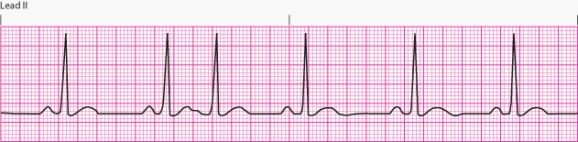
A) Sinus rhythm with PACs
B) Normal sinus rhythm
C) Sinus tachycardia
D) Sinus bradycardia
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse notices ventricular tachycardia on the heart monitor.When the patient is assessed,the patient is found to be unresponsive with no pulse.The nurse should
A) treat with intravenous amiodarone or lidocaine.
B) begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation and advanced life support.
C) provide electrical cardioversion.
D) ignore the rhythm because it is benign.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse caring for patients with cardiac monitoring understands that when an electrical signal is aimed directly at the positive electrode,the inflection will be:
A) negative.
B) upside down.
C) upright.
D) equally positive and negative.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nurse caring for patients on cardiac monitors assesses the patient with a prolonged QT interval for
A) electrolyte disturbances such as hypokalemia.
B) symptomatic bradycardias.
C) the development of lethal dysrhythmias.
D) difficulty maintaining the blood pressure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm:
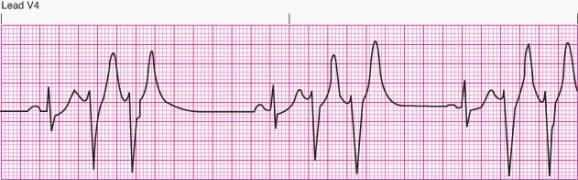
A) Sinus rhythm with multifocal premature ventricular contractions
B) Sinus rhythm with unifocal premature ventricular contractions
C) Sinus rhythm with bigeminal premature ventricular contractions
D) Sinus rhythm with paired premature ventricular contractions (couplets)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rhythm on the cardiac monitor is showing numerous pacemaker spikes,but no P waves or QRS complexes following the spikes.The nurse recognizes this as:
A) normal pacemaker function.
B) failure to capture.
C) failure to pace.
D) failure to sense.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The patient's heart rate is 70 beats per minute,but the P waves come after the QRS complex.The nurse correctly determines that the patient's heart rhythm is
A) a normal junctional rhythm.
B) an accelerated junctional rhythm.
C) a junctional tachycardia.
D) atrial fibrillation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interpret the following rhythm:
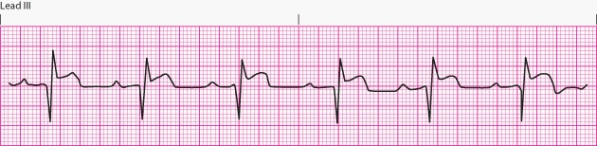
A) Normal sinus rhythm
B) Sinus rhythm with second-degree AV block
C) Complete heart block
D) Sinus rhythm with first-degree AV block
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 59
Related Exams