A) they are engaged in predatory pricing.
B) these firms have monopolized the industry.
C) they are creating entry barriers to prevent entry by new firms.
D) they are perfect competitors and they are unable to set the price.
E) there is tacit collusion among these firms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows selected cost and revenue curves for a firm in a monopolistically competitive industry.
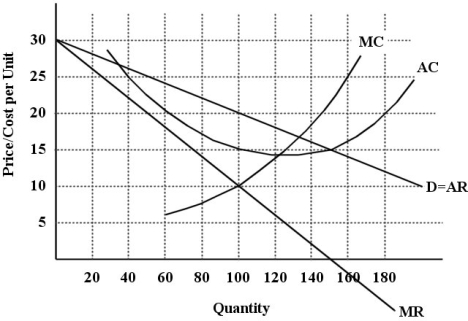 FIGURE 11- 1
-An imperfectly competitive industry is often allocatively inefficient when compared to the performance of a competitive industry,because imperfect competitors
FIGURE 11- 1
-An imperfectly competitive industry is often allocatively inefficient when compared to the performance of a competitive industry,because imperfect competitors
A) make profits.
B) operate in the global economy.
C) set price above the marginal cost.
D) obtain economies of scale.
E) maximize profits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
By calculating a concentration ratio,economists measure the
A) fraction of total industry sales accounted for by the largest firms.
B) degree to which a monopolist's output is lower than in perfect competition.
C) concentration of firms in one geographic location.
D) control of a monopolist over its input prices.
E) degree to which firms in the industry use similar technologies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The presence of significant scale economies in an industry implies that
A) barriers to entry in the industry are non- existent.
B) the firms in the industry will behave as perfect competitors.
C) a large share of the market is required by each firm to achieve the lowest possible cost per unit.
D) this industry is more efficient than others.
E) the minimum efficient scale of operation occurs at fairly low output levels.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
FIGURE 11- 2 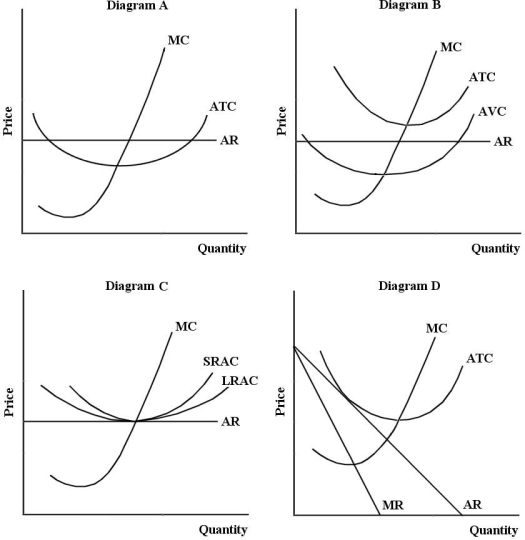 -Assume that the world's largest smart- phone producers (Apple,Nokia,Samsung,etc.) operate in an oligopolistic industry.In the long run,which of the following is the most important form of competition between these firms?
-Assume that the world's largest smart- phone producers (Apple,Nokia,Samsung,etc.) operate in an oligopolistic industry.In the long run,which of the following is the most important form of competition between these firms?
A) tacit collusion
B) brand proliferation
C) predatory pricing
D) advertising
E) product innovation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the following,which is the best example of a monopolistically competitive firm?
A) Burger King
B) a local hair salon
C) Apple
D) a PEI potato farmer
E) Air Canada
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the market shares for the only firms in a domestic cement market. TABLE 11- 1 -Refer to Table 11- 1.The eight- firm concentration ratio in this industry is %.
A) 85
B) 92
C) 45
D) 67
E) 100
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm.
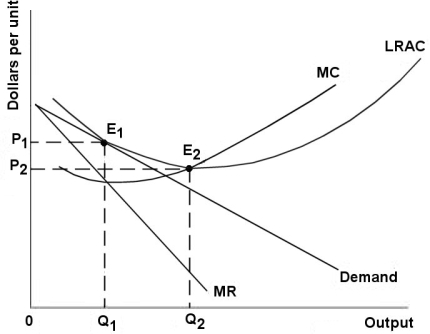 FIGURE 11- 3
-The following statements describe a cooperative equilibrium in an oligopoly where the firms are jointly maximizing profits by restricting output.Which statement is false?
FIGURE 11- 3
-The following statements describe a cooperative equilibrium in an oligopoly where the firms are jointly maximizing profits by restricting output.Which statement is false?
A) MR > MC for each individual firm.
B) No individual firm will have an incentive to change output.
C) An individual firm could increase profits by cheating.
D) The firms in the industry will jointly be earning monopoly profits.
E) P > MC for each individual firm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
"Brand proliferation" in an oligopolistic industry
A) allows easier entry to a new entrant with small sales.
B) allows firms to cooperate to maximize their joint profits.
C) will generally reduce the expected market share of new entrants to the industry.
D) allows new entrants to the industry to gain significant market share.
E) can shift the average total cost curve down and raise the overall minimum scale of operation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the 2- firm concentration ratio (measuring output) in a Canadian manufacturing industry is over 90%.Why might the market power of these 2 firms be less than the concentration ratio suggests?
A) A high concentration ratio usually indicates low degrees of market power.
B) A 2- firm concentration ratio does not provide enough information.
C) The product is purely domestic and there is no international trade.
D) The product is traded internationally and the two Canadian firms compete with many global rivals.
E) The relevant market is regional and so the concentration ratio is not relevant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the market shares for the only firms in a domestic cement market. TABLE 11- 1 -Oligopolists make decisions after taking into account the expected reaction of their competitors.In doing this,oligopolists are exhibiting
A) non- cooperative behaviour.
B) collusive behaviour.
C) cooperative behaviour.
D) strategic behaviour.
E) non- strategic behaviour.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
-Refer to Table 11- 2.If Firm A is indifferent between cheating or cooperating when Firm B chooses to cooperate,x must be equal to
A) 0.
B) 10.
C) 40.
D) 20.
E) 30.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm.
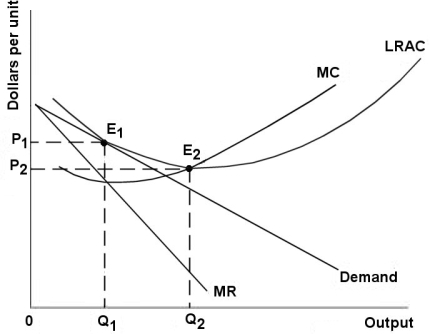 FIGURE 11- 3
-Refer to Figure 11- 3.A monopolistically competitive firm is allocatively inefficient because in the long- run equilibrium
FIGURE 11- 3
-Refer to Figure 11- 3.A monopolistically competitive firm is allocatively inefficient because in the long- run equilibrium
A) MC is greater than price.
B) LRAC is not at its minimum.
C) price is greater than LRAC at Q1.
D) price is greater than MC at Q1.
E) None of the above - the long- run equilibrium is allocatively efficient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose there are many independent dry cleaners in your city,each of which provides essentially the same service.However,one offers local delivery,another offers free coffee in the shop,while another offers one- hour dry cleaning.Which of the following statements explains what is happening in this market?
A) These firms are monopolistically competitive and are attempting to differentiate their product.
B) These firms are perfectly competitive and are attempting to increase sales and maximize their profits.
C) These firms are perfectly competitive and are engaging in strategic behaviour.
D) These firms are oligopolistic and are engaging in strategic behaviour.
E) These firms are perfectly competitive and are engaging in non- price competition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
FIGURE 11- 2 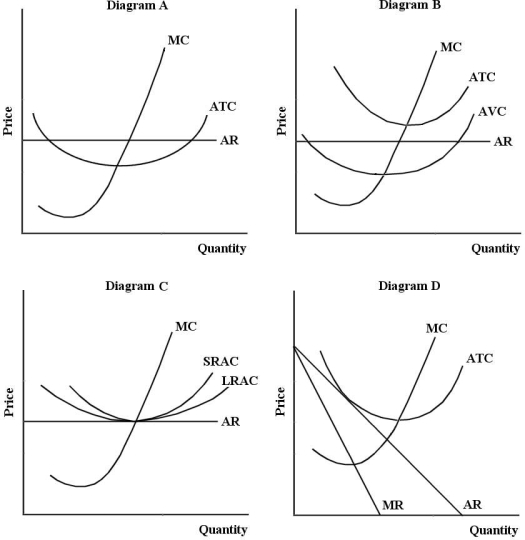 -Consider the following characteristics of a particular industry: - the four- firm concentration ratio is 78% (in the relevant market)
- each firm produces output where P > MC
- the products are highly differentiated This industry is likely to be
-Consider the following characteristics of a particular industry: - the four- firm concentration ratio is 78% (in the relevant market)
- each firm produces output where P > MC
- the products are highly differentiated This industry is likely to be
A) perfectly competitive.
B) monopolistic.
C) one where each firm has limited market power.
D) an oligopoly.
E) a cartel.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 115 of 115
Related Exams