A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Table 6.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 6.1 -Refer to Table 6.1. Diminishing marginal utility sets in after the ________ soda per day.
A) first
B) second
C) third
D) fourth
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The price of leisure is the wage rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 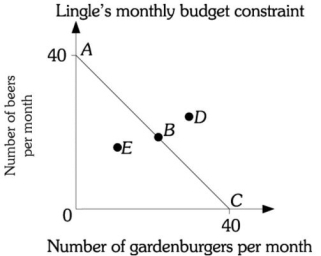 Figure 6.2
-Refer to Figure 6.2. Assume Mr. Lingle is on budget constraint AC. If the price of a beer is $5, Mr. Lingle's monthly income is
Figure 6.2
-Refer to Figure 6.2. Assume Mr. Lingle is on budget constraint AC. If the price of a beer is $5, Mr. Lingle's monthly income is
A) $40.
B) $80.
C) $100.
D) $200.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.14 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 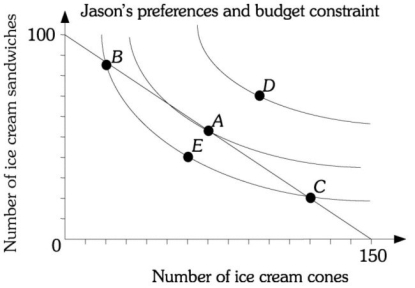 Figure 6.14
-Refer to Figure 6.14. Jason cannot afford the bundle represented by point
Figure 6.14
-Refer to Figure 6.14. Jason cannot afford the bundle represented by point
A) E.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For Matthew, the marginal utility of the 9th soda in a day is positive and the marginal utility of the 10th soda in a day is zero. This
A) implies that Matthew's demand curve for sodas per day will become upward sloping at 10 sodas per day.
B) is impossible because each additional unit of consumption of any good must provide positive marginal utility.
C) implies that at a zero price Matthew's demand curve will intersect the quantity axis at 10.
D) implies that Matthew maximizes utility by consuming 9 sodas per day.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 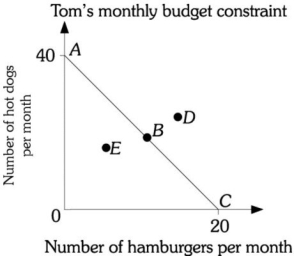 Figure 6.1
-Refer to Figure 6.1. Along budget constraint AC, the opportunity cost of one hot dog
Figure 6.1
-Refer to Figure 6.1. Along budget constraint AC, the opportunity cost of one hot dog
A) is 1/4 of a hamburger.
B) is 1/2 of a hamburger.
C) is 2 hamburgers.
D) changes as you move down along the budget constraint.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume leisure is an inferior good instead of a normal good. The income effect of a wage increase will lead to a ________ demand for leisure and a ________ labor supply.
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) lower; lower
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The law of diminishing marginal utility implies that as a household consumes more of a product, its total utility will increase by larger amounts -assuming marginal utility remains positive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Table 6.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 6.1 -Refer to Table 6.1. Assume that a store is giving hamburgers and sodas away for free. Consumers can have as many sodas and hamburgers as they want, but the food has to be consumed one unit at a time. If George has already had one soda and two hamburgers, then George should
A) next consume a soda to maximize his utility.
B) next consume a hamburger to maximize his utility.
C) be indifferent between consuming the second soda or the third hamburger.
D) consume neither another soda nor another hamburger to maximize his utility.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If MUx/Px exceeds MUy/Py, then a household can increase its utility by spending more on Y and less on X.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 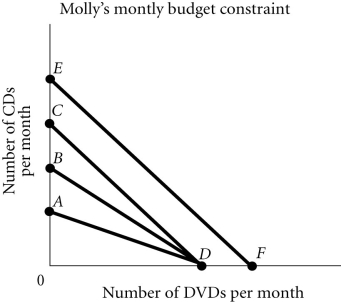 Figure 6.5
-Refer to Figure 6.5. Molly's budget constraint is EF. If her income decreases while the price of the goods are unchanged, her new budget constraint is
Figure 6.5
-Refer to Figure 6.5. Molly's budget constraint is EF. If her income decreases while the price of the goods are unchanged, her new budget constraint is
A) AD.
B) BD.
C) CD.
D) It is not shown on this graph.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Assuming a perfectly competitive market implies that households have perfect knowledge of qualities and prices of everything available in the market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.8 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 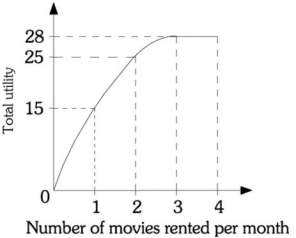 Figure 6.8
-Refer to Figure 6.8. The marginal utility of the third movie rental is
Figure 6.8
-Refer to Figure 6.8. The marginal utility of the third movie rental is
A) 0.
B) 3.
C) 12.
D) 28.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price of an inferior good rises, the income effect will result in households buying ________ of the good and the substitution effect will result in households buying ________ of the good.
A) more; more
B) more; less
C) less; more
D) less; less
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The diamond/water paradox is only true in theory, but no real-world examples have yet to be discovered.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Table 6.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 6.2 -Refer to Table 6.2. If the price of a candy bar is $1, the price of a hot dog is $2, and Aaron has $6 of income, Aaron's utility-maximizing combination of candy bars and hot dogs per day is
A) 1 candy bar and 2 hot dogs.
B) 4 candy bars and 1 hot dog.
C) 2 candy bars and 1.5 hot dogs.
D) indeterminate from this information.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 6.1
-Refer to Figure 6.1. Assume Tom is on budget constraint AC and the price of a hamburger is $8.00. Tom's monthly income is
Figure 6.1
-Refer to Figure 6.1. Assume Tom is on budget constraint AC and the price of a hamburger is $8.00. Tom's monthly income is
A) $2.50.
B) $20.
C) $80.
D) $160.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 6.2
-Refer to Figure 6.2. Assume Mr. Lingleʹs budget constraint is AC. He will have leftover income if he purchases the bundle represented by point
Figure 6.2
-Refer to Figure 6.2. Assume Mr. Lingleʹs budget constraint is AC. He will have leftover income if he purchases the bundle represented by point
A) A.
B) B.
C) E.
D) D.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 6.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.  Figure 6.5
-Refer to Figure 6.5. Molly's budget constraint is EF. If her income decreases while the price of the goods are unchanged, her new budget constraint could be
Figure 6.5
-Refer to Figure 6.5. Molly's budget constraint is EF. If her income decreases while the price of the goods are unchanged, her new budget constraint could be
A) AD.
B) BD.
C) CD.
D) Her new possible budget constraint is not shown on this graph.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 272
Related Exams