A) Compare the genome sequences of different species to identify conserved amino acids
B) Filter the results to include only common polymorphisms
C) Determine genotypes of parents and children at all SSR loci
D) Use microarrays to identify silent mutations
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which polymorphism is most likely to affect an individual's phenotype?
A) An SNP in an intron of a protein-coding gene
B) An SSR within a telomeric sequence
C) A DIP in an intragenic region between genes
D) An SNP in the start codon of a protein-coding gene
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Examine this pedigree that shows segregation of Huntington disease and the DNA marker G8.What was the most likely genotype of individual V-3 at the DNA marker? 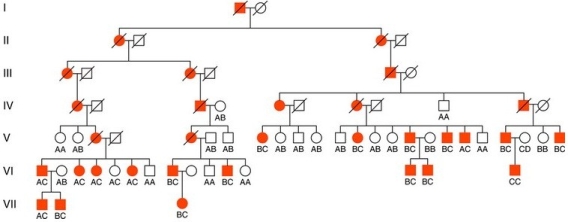
A) BC
B) AB
C) CC
D) AC
E) All of the possible genotypes are equally likely.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most polymorphisms do not result in a phenotypic difference because they are typically
A) nonsense mutations.
B) either missense or neutral mutations.
C) either silent mutations or are in non-coding regions.
D) either missense mutations or are in promoter regions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many bases do deletion-insertion polymorphisms (DIPs) most frequently involve?
A) 1-2
B) multiples of 3
C) 10-100
D) more than 100
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How can databases of variants be used to help pinpoint a disease-causing mutation? (Select all that apply. )
A) Polymorphisms found in individuals that do not have the syndrome can be eliminated from consideration.
B) Common polymorphisms are unlikely to cause a rare disease and they can be eliminated from consideration.
C) Some amino acids are conserved in genes across species; mutations in conserved amino acids are not likely to cause disease.
D) Mutations that occur between genes are most likely to cause a genetic disease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The classical form of the metabolic disease phenylketonuria is caused by a mutation in the gene encoding the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) , which converts phenylalanine to tyrosine.A variant form of phenylketonuria is caused by a mutation in a separate gene that encodes a different enzyme involved in the synthesis of a cofactor needed for PAH to function.Which of the following phenomena is illustrated by these two forms of phenylketonuria?
A) Allelic heterogeneity
B) Compound heterozygosity
C) Locus heterogeneity
D) Anonymous polymorphism
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Allele-specific oligonucleotides (ASO) for the normal and disease alleles of a gene are in one section of a microarray.The disease is a recessive trait.If a probe made from an individual's genomic DNA hybridizes with both ASOs, what can be inferred about the individual?
A) The individual has two normal alleles.
B) The individual has the disease.
C) 50% of the individual's children are expected to be carriers.
D) One of the individual's parents has the disease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which are typically used for positional cloning of a disease gene in humans? (Select all that apply. )
A) analysis of several human pedigrees in which the disease is segregating
B) genotyping of diseased and healthy individuals at millions of anonymous polymorphisms using microarrays
C) sequencing candidate genes
D) a multigenerational selective breeding program
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identifying candidates for a disease gene by positional cloning depends on distinguishing DNA markers that are close to the disease gene from markers that are far away.When the disease gene is close to a marker, there will be
A) a high number of mutations in the intervening DNA.
B) a low rate of recombination between the disease gene and the marker.
C) many alleles at the marker locus.
D) a high chance of locus heterogeneity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Positional cloning depends on knowing what?
A) the function of a gene
B) the expression pattern of a gene
C) the map location of markers that are linked to a gene
D) the sequence of a gene.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement about SNPs in the human genome is true?
A) Most SNPs have an effect on phenotype.
B) Any two human genome copies will have on average 3 million single nucleotide polymorphisms.
C) SNPs refer only to deletions or insertions, not base substitutions.
D) Most SNPs are located in the introns of genes, and thus effect phenotype.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which does a successful PCR require?
A) at least 100 starting DNA template molecules
B) some sequence information about the region to be amplified
C) a cloned cDNA of the region to be amplified
D) a double-stranded DNA template of at least 100 kb to amplify
E) an undamaged DNA template with intact chromosomes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most common mutant allele of the PAH gene, which is responsible for the metabolic disorder PKU, has a SNP in the splice donor site of one intron.What is the simplest way to detect this allele?
A) PCR using genomic DNA as template and two primers, one on either side of the SNP, followed by gel electrophoresis
B) PCR using genomic DNA as template and two primers, one complementary to the region containing the SNP, followed by gel electrophoresis
C) PCR using two primers, one on either side of the SNP, followed by sequencing the PCR products
D) Direct exome sequencing using a microarray
E) Whole-genome sequencing
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In 2013, a man was arrested for transporting 400 pounds of marijuana across state lines.His DNA was tested, entered into the CODIS database, and found to match the crime scene sample in the Margaret Binkele case.What additional evidence would increase your confidence that the man arrested for transporting marijuana murdered Margaret Binkele? (Select all that apply. )
A) A receipt that showed the man used his credit card in Texas on the night of the murder
B) The genotype at additional SSR loci that show a match at seven and a mismatch at three loci.
C) Discovery of the man's fingerprints on the murder weapon
D) A match between his blood and the crime scene sample at more than three SSR loci
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Linkage between a gene of interest and a DNA marker is being studied. A mating results in 19 parental and 1 recombinant offspring. -The results of this mating are sufficient to conclude with confidence that the gene of interest and the DNA marker are linked.
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which are limitations of preimplantation embryo diagnosis? (Select all that apply. )
A) The technique is technologically complex and expensive.
B) Only certain well-defined genetic diseases can be tested.
C) The test increases the rate of twin births.
D) Removal of one cell from an eight-cell embryo results in permanent damage to the embryo.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Linkage between a gene of interest and a DNA marker is being studied. A mating results in 6 parental and 3 recombinant offspring -What is the maximum Lod score for this mating?
A) 0.22
B) 1.1
C) 6.3
D) 11
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is an example of a SNP? (Select all that apply. )
A) A single base near the neurofibromatosis gene can be a G or a T; phenotype is not affected.
B) A single base change in the gene for β globin changes an amino acid and results in sickle cell anemia.
C) Individuals with Huntington disease have more trinucleotide repeats in the coding region of the HD gene than normal individuals.
D) The most common cystic fibrosis allele has a deletion of three base pairs in the coding region of the CFTR gene.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Linkage between a gene of interest and a DNA marker is being studied. A mating results in 19 parental and 1 recombinant offspring. -What is the maximum Lod score for linkage at this locus?
A) 0.22
B) 1.1
C) 6.3
D) 11
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 38
Related Exams