A) A
B) B
C) E
D) G
E) H
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The signal to excite a muscle cell must cross the neuromuscular junction by the diffusion of acetylcholine across the
A) motor neuron axon.
B) synaptic cleft.
C) sarcolemma.
D) synaptic vesicles.
E) myofibril.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For every nerve that penetrates a skeletal muscle, there are in general how many arteries and veins?
A) one artery and one or two veins
B) two arteries and two veins
C) three arteries and two veins
D) one artery and three veins
E) one artery and a varied amount of veins
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hypertrophy is
A) an increase in the size of muscle fibers.
B) a decrease in the size of muscle fibers.
C) an increase in the number of muscle fibers.
D) a decrease in the number of muscle fibers.
E) a loss in size and strength of muscle fibers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is occurring during this period of a muscle twitch contraction? 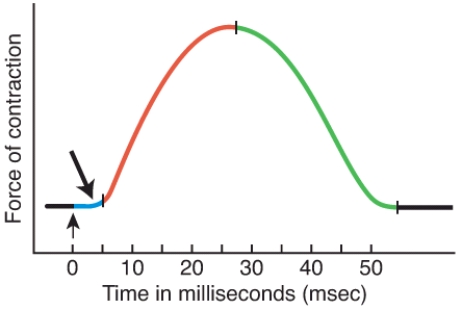
A) The muscle action potential sweeps along the sarcolemma and calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
B) Crossbridge attachments form, and repetitive power strokes occur.
C) The level of Ca2+ in the sarcoplasm decreases, because it is being actively transported back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum and bound to calsequestrin.
D) The muscle fiber relaxes as myosin heads detach from the actin filaments.
E) Acetylcholinesterase is preventing the ligand gated channels at the motor end plate from binding to ACh.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This consists of a somatic motor neuron plus all the skeletal muscle fibers it stimulates.
A) sarcomere
B) motor unit
C) neuromuscular junction
D) somatic motor neuron
E) muscle fiber
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The different types of muscle tissue differ from each other by:
A) microscopic anatomy
B) location
C) type of control
D) both microscopic anatomy and location
E) all of these choices
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a correct structure and tissue type pairing?
A) endomysium : loose areolar connective tissue
B) perimysium : dense irregular connective tissue
C) tendon : dense regular connective tissue
D) sarcolemma : loose areolar connective tissue
E) epimysium: dense irregular connective tissue
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A single, brief contraction of all muscle fibers in a motor unit in response to a single action potential is called:
A) recovery oxygen uptake
B) motor unit movement
C) muscle fatigue
D) refractory period
E) twitch contraction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the diagram, what letter indicates a triad? 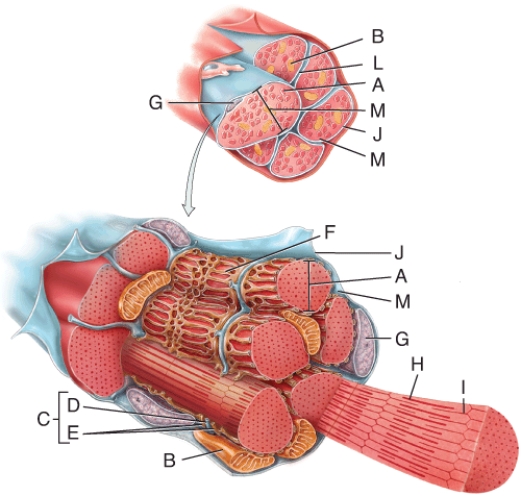
A) G
B) E
C) D
D) F
E) C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the diagram, where is the skeletal muscle fiber? 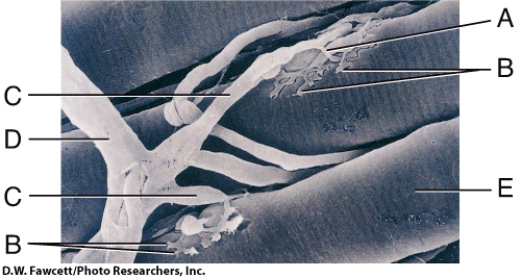
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many molecules of acetylcholine need to bind to open the ion channel of the ACh receptor?
A) 34
B) 5
C) 10
D) an unknown amount
E) 2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This is also referred to as the period of lost excitability.
A) refractory period
B) contraction period
C) latent period
D) relaxation period
E) wave summation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calcium ions bind to the ___ molecule in skeletal muscle cells.
A) actin
B) troponin
C) tropomyosin
D) myosin
E) titin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the diagram, what is made from dense regular connective tissue? 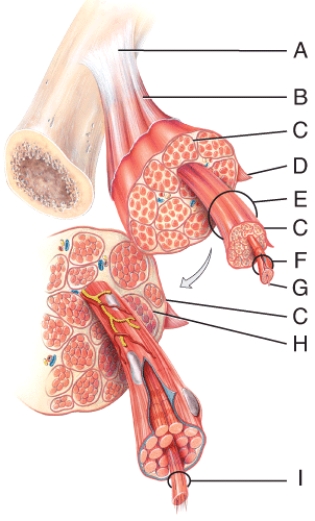
A) A
B) H
C) C
D) D
E) All of these choices
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the diagram, where is the muscle fiber located? 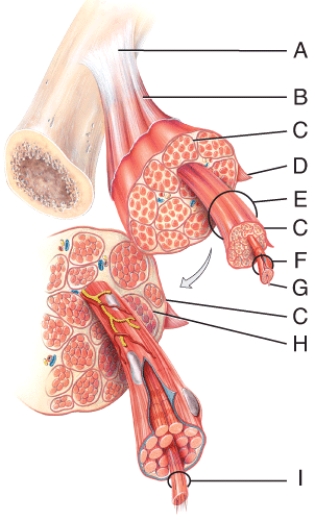
A) E
B) F
C) G
D) B
E) I
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
During isotonic contraction, the heavier the load, the faster the velocity of muscle shortening.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Myofibrils contain
A) contractile proteins.
B) regulatory proteins.
C) structural proteins.
D) all of these choices.
E) none of these choices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After the fusion of myoblasts, the muscle fiber loses its ability to do what?
A) grow
B) lengthen
C) contract
D) go through mitosis
E) all of these choices
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
These are the contractile organelles of the muscle fiber.
A) myofibrils
B) myoglobin
C) mitochondria
D) Z disc
E) M line
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 93
Related Exams