A) No; antibiotics work by inhibiting enzymes specific to bacteria. Antibiotics have no effect on eukaryotic or virally encoded enzymes.
B) No; antibiotics do not kill viruses because viruses do not have DNA or RNA.
C) Yes; antibiotics activate the immune system, and this decreases the severity of the infection.
D) Yes; antibiotics can prevent viral entry into the cell by binding to host-receptor proteins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct regarding viral infections in plants?
A) They can be controlled with antibiotics.
B) They can spread within a plant via plasmodesmata.
C) They have little effect on plant growth.
D) They are not spread by animals.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do RNA viruses appear to have higher rates of mutation?
A) RNA nucleotides are more unstable than DNA nucleotides.
B) Replication of their genomes does not involve proofreading.
C) RNA viruses can incorporate a variety of nonstandard bases.
D) RNA viruses are more sensitive to mutagens.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements accurately describes the lysogenic cycle of lambda (λ) phage?
A) After infection, the viral genes immediately turn the host cell into a lambda-producing factory, and the host cell then lyses.
B) Most of the prophage genes are activated by the product of a particular prophage gene.
C) The phage genome is integrated in the host chromosome where it is replicated along with the host genome.
D) The phage DNA is copied and exits the cell as a phage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between vertical and horizontal transmission of plant viruses is that vertical transmission is ________.
A) transmission of a virus from a parent plant to its progeny, and horizontal transmission is one plant spreading the virus to another plant
B) the spread of viruses from upper leaves to lower leaves of the plant, and horizontal transmission is the spread of a virus among leaves at the same general level
C) the spread of viruses from trees and tall plants to bushes and other smaller plants, and horizontal transmission is the spread of viruses among plants of similar size
D) the transfer of DNA from a plant of one species to a plant of a different species, and horizontal transmission is the spread of viruses among plants of the same species
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
RNA viruses require their own supply of certain enzymes because
A) host cells rapidly destroy the viruses.
B) host cells lack enzymes that can replicate the viral genome.
C) these enzymes translate viral mRNA into proteins.
D) these enzymes penetrate host cell membranes.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A population of viruses with similar characteristics is called a ________.
A) class
B) species
C) type
D) genome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure to answer the question.
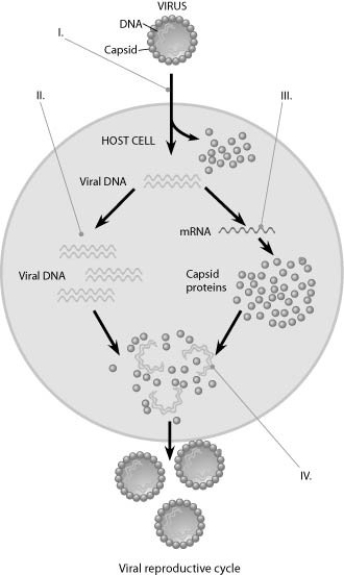 In the figure, at the arrow marked II, what enzyme is being utilized?
In the figure, at the arrow marked II, what enzyme is being utilized?
A) reverse transcriptase
B) viral DNA polymerase
C) host cell DNA polymerase
D) host cell RNA polymerase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A researcher lyses a cell that contains nucleic acid molecules and capsomeres of tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) . The cell contents are left in a covered test tube overnight. The next day this mixture is sprayed on tobacco plants. What would you expect to happen to the plants that were sprayed with the mixture?
A) The plants would develop some but not all of the symptoms of the TMV infection.
B) The plants would develop the typical symptoms of TMV infection.
C) The plants would not show any disease symptoms.
D) The plants would become infected, but extracts from these plants would be unable to infect other plants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In many ways, the regulation of the genes of a particular group of viruses will be similar to the regulation of the host genes. Therefore, which of the following regulation mechanisms would you expect of the genes of a bacteriophage?
A) regulation via acetylation of histones
B) positive control mechanisms rather than negative
C) control of more than one gene in an operon
D) reliance on transcription activators
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To cause a human pandemic, the H5N1 avian flu virus would have to
A) spread to primates such as chimpanzees.
B) develop into a virus with a different host range.
C) become capable of human-to-human transmission.
D) become much more pathogenic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes within viral replication is the greatest source of genetic variation in RNA virus populations?
A) High mutation rate due to lack of proofreading of RNA genome replication errors.
B) Transcription from the host cell RNA polymerase introduces numerous mutations.
C) Capsid proteins from the host cell can replace the viral capsid.
D) Viral RNA is translated by host cell ribosomes.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is difference between an epidemic and a pandemic?
A) An epidemic is a disease; a pandemic is a treatment.
B) An epidemic is restricted to a local region; a pandemic is global.
C) An epidemic has low mortality; a pandemic has higher mortality.
D) An epidemic is caused by a bacterial infection; a pandemic is caused by a viral infection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figures to answer the question.
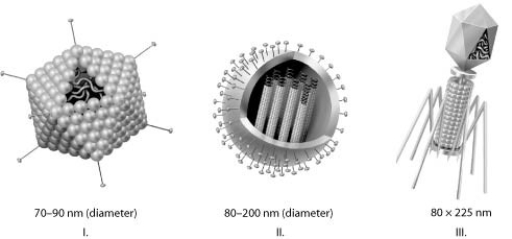 Which of the three types of viruses shown would you expect to include glycoproteins?
Which of the three types of viruses shown would you expect to include glycoproteins?
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and II only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following human diseases is caused by a virus that requires reverse transcriptase to transcribe its genome inside the host cell?
A) herpes
B) AIDS
C) smallpox
D) influenza
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question. The herpes viruses are important enveloped DNA viruses that cause disease in vertebrates and in some invertebrates such as oysters. Some of the human forms are herpes simplex virus (HSV) types I and II, causing facial and genital lesions, and the varicella zoster virus (VSV) , causing chicken pox and shingles. Each of these three actively infects nervous tissue. Primary infections are fairly mild, but the virus is not then cleared from the host; rather, viral genomes are maintained in cells in a latent phase. The virus can later reactivate, replicate again, and infect others. If scientists are trying to use what they know about the herpes simplex virus to devise a means of protecting other people from being infected, which of the following treatments would have the best chance of lowering the number of new cases of infection?
A) Vaccinate of all persons with preexisting cases of herpes simplex virus.
B) Interfere with new viral replication in preexisting cases of herpes simplex virus.
C) Treat herpes simplex virus lesions to shorten the breakout.
D) Educate people about avoiding sources of infection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are prions?
A) mobile segments of DNA
B) tiny circular molecules of RNA that can infect plants
C) viral DNA that attaches itself to the host genome and causes disease
D) misfolded versions of normal proteins that can cause disease
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A virus consisting of a single strand of RNA, which is reverse transcribed into complementary DNA, is referred to as a ________.
A) protease
B) retrovirus
C) bacteriophage
D) non-enveloped virus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements supports the argument that viruses are nonliving?
A) They do not carry out metabolic processes.
B) Their DNA does not encode proteins.
C) They have RNA rather than DNA.
D) They do not evolve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the treatments listed to answer the question. You isolate an infectious substance capable of causing disease in plants, but you do not know whether the infectious agent is a bacterium, virus, or prion. You have four methods at your disposal to analyze the substance and determine the nature of the infectious agent. I.Treat the substance with enzymes that destroy all nucleic acids, and then determine whether the substance is still infectious. II.Filter the substance to remove all elements smaller than what can be easily seen under a light microscope. III.Culture the substance on nutritive medium, away from any plant cells. IV.Treat the sample with proteases that digest all proteins, and then determine whether the substance is still infectious. If you already know that the infectious agent was either bacterial or viral, which method(s) listed above would allow you to distinguish between these two possibilities?
A) I
B) II
C) II or III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 54
Related Exams