A) chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision
B) dendrites, a cell body, and an axon
C) a presynaptic cell, neurotransmitters, and a postsynaptic cell
D) sensory reception, an integrating center, and effectors (motor neurons)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a particular neurotransmitter causes an IPSP in postsynaptic cell X and an EPSP in postsynaptic cell Y. A likely explanation is that
A) the threshold value in the postsynaptic membrane is different for cell X and cell Y.
B) the axon of cell X is myelinated, but that of cell Y is not.
C) only cell Y produces an enzyme that terminates the activity of the neurotransmitter.
D) cells X and Y express different receptor molecules for this particular neurotransmitter.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most of the neurons in the human central nervous system are ________.
A) sensory neurons
B) motor neurons
C) interneurons
D) peripheral neurons
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a simple synapse, neurotransmitter chemicals are released by ________.
A) the presynaptic membrane
B) axon hillocks
C) cell bodies
D) ducts on the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A graded hyperpolarization of a membrane can be induced by ________.
A) increasing its membrane's permeability to Na⁺
B) decreasing its membrane's permeability to Cl⁻
C) increasing its membrane's permeability to Ca⁺⁺
D) increasing its membrane's permeability to K⁺
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following will increase the speed of an action potential moving down an axon? I.Action potentials move faster in wider axons. II.Action potentials move faster in axons lacking potassium ion channels. III.Action potentials move faster in myelinated axons.
A) only I and II
B) only II and III
C) only I and III
D) I, II, and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neurotransmitters can affect postsynaptic cells by ________. I.initiating signal transduction pathways in the cells II.causing molecular changes in the cells III.altering ion channel proteins IV.altering the permeability of the cells
A) I and III
B) II and IV
C) III and IV
D) I, II, III, and IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the following graph of an action potential to answer the question.
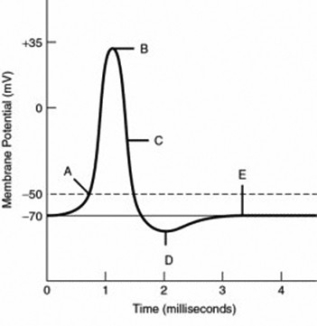 At label ________, the cell is not hyperpolarized; however, repolarization is in progress, as the sodium channels are inactivated or becoming inactivated, and many potassium channels have opened.
At label ________, the cell is not hyperpolarized; however, repolarization is in progress, as the sodium channels are inactivated or becoming inactivated, and many potassium channels have opened.
A) B
B) C
C) D
D) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Action potentials move along axons ________.
A) more slowly in axons of large than in small diameter
B) by activating the sodium-potassium "pump" at each point along the axonal membrane
C) more rapidly in myelinated than in unmyelinated axons
D) by reversing the concentration gradients for sodium and potassium ions
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Conduction and refractory periods (states) are typical of ________.
A) action potentials
B) graded hyperpolarizations
C) excitatory postsynaptic potentials
D) threshold potentials
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When two excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) occur at a single synapse so rapidly in succession that the postsynaptic neuron's membrane potential has not returned to the resting potential before the second EPSP arrives, the EPSPs add together producing ________.
A) temporal summation
B) spatial summation
C) tetanus
D) the refractory state
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tetrodotoxin blocks voltage-gated sodium channels, and ouabain blocks sodium-potassium pumps. If you added both tetrodotoxin and ouabain to a solution containing neural tissue, what responses would you expect?
A) immediate loss of resting potential
B) immediate loss of action potential with gradual shift of resting potential
C) slow decrease of resting potential and action potential amplitudes
D) No effect; the substances counteract each other.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The point of connection between two communicating neurons is called the ________.
A) axon hillock
B) dendrite
C) synapse
D) cell body
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The motor (somatic nervous) system can alter the activities of its targets, the skeletal muscle fibers, because ________.
A) it is electrically coupled by gap junctions to the muscles
B) its signals bind to receptor proteins on the muscles
C) its signals reach the muscles via the blood
D) it is connected to the internal neural network of the muscles
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neurotransmitters categorized as inhibitory are expected to ________.
A) act independently of their receptor proteins
B) close potassium channels
C) open sodium channels
D) hyperpolarize the membrane
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After the depolarization phase of an action potential, the resting potential is restored by ________.
A) the opening of voltage-gated potassium channels and the inactivation of sodium channels
B) a decrease in the membrane's permeability to potassium and chloride ions
C) a brief inhibition of the sodium-potassium pump
D) the opening of more voltage-gated sodium channels
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fastest possible conduction velocity of action potentials is observed in ________.
A) thin, unmyelinated neurons
B) thin, myelinated neurons
C) thick, unmyelinated neurons
D) thick, myelinated neurons
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The operation of the sodium-potassium pump moves ________.
A) sodium and potassium ions into the cell
B) sodium and potassium ions out of the cell
C) sodium ions into the cell and potassium ions out of the cell
D) sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two fundamental concepts about the ion channels of a "resting" neuron are that the channels ________.
A) are always open, but the concentration gradients of ions frequently change
B) are always closed, but ions move closer to the channels during excitation
C) are open or closed depending on their type, and are specific as to which ion can traverse them
D) open in response to stimuli, and then close simultaneously, in unison
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a simple synapse, neurotransmitter chemicals are received by ________.
A) the presynaptic membrane
B) dendrites
C) axon hillocks
D) cell bodies
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 68
Related Exams