A) Two cases of soda for every three gallons of milk
B) One case of soda for every one and a half gallons of milk
C) Three cases of soda for every four and a half gallons of milk
D) All of these accurately reflect Imani's tradeoff.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown describes the different combinations of goods that Jack can consume, given that he has $10 to spend on these two items.
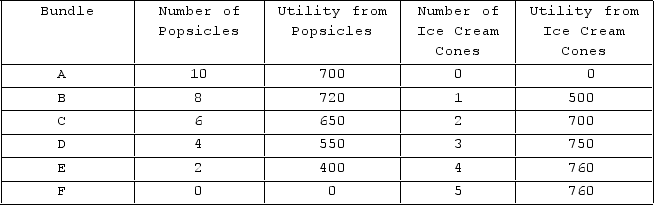 If Jack decides to consume bundle D, we can conclude that he:
If Jack decides to consume bundle D, we can conclude that he:
A) still has money left to spend.
B) is not maximizing his utility.
C) could consume more of both goods.
D) All of these are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After browsing his cabinets to see what meals he can make, Ken is deciding whether to make tacos or spaghetti for dinner. If Ken makes spaghetti, we can conclude:I. Ken would receive zero utility from eating tacos.II. Eating spaghetti for dinner will give Ken more utility than eating tacos.III. Eating spaghetti for dinner will give Ken positive utility.
A) III only
B) II only
C) II and III only
D) I, II and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Linus has just watched two hours of TV. Which of the following is likely true?
A) His second hour of watching TV reduced his total utility.
B) His second hour of watching TV added less to his total utility than did the first.
C) His third hour of watching TV will decrease his total utility.
D) His third hour of watching TV will increase his total utility by at least as much as the second.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
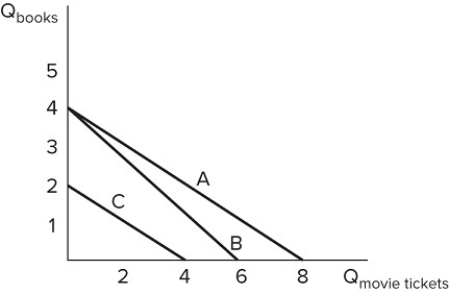 Assume Claudia's budget constraint is represented by line A in the graph shown. Which of the following would cause Claudia's budget constraint to shift to line C?
Assume Claudia's budget constraint is represented by line A in the graph shown. Which of the following would cause Claudia's budget constraint to shift to line C?
A) The price of books decreases.
B) The price of movie tickets decreases.
C) Claudia's preferences for these two goods decrease.
D) Claudia's income decreases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
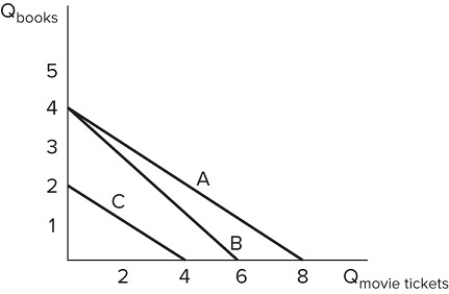 Assume Alan's budget constraint is represented by line A in the graph shown. Which of the following would cause Alan's budget constraint to move to line B?
Assume Alan's budget constraint is represented by line A in the graph shown. Which of the following would cause Alan's budget constraint to move to line B?
A) Alan experiences a drop in income.
B) The price of books increases.
C) Alan decides he doesn't like going to the movies as much as he used to.
D) The price of movie tickets increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pranav is deciding what to drink from a cooler that contains cans of soda pop and iced tea. When Pranav chooses iced tea, we assume that he will receive more utility from drinking iced tea than soda pop. Which economic concept is this conclusion based on?
A) Revealed preference
B) Utility minimization
C) Satisfaction scales
D) Rational behavior
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is reciprocity?
A) Responding to another's actions with a similar action.
B) Deriving utility from an action that will cause another's utility to increase.
C) Doing good things for people and asking nothing in return.
D) Deriving utility from a stranger's actions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Manu offers to buy his friend lunch after helping him study for an exam. This is an example of the economic concept of:
A) marginal utility.
B) altruism.
C) reciprocity.
D) a Veblen good.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
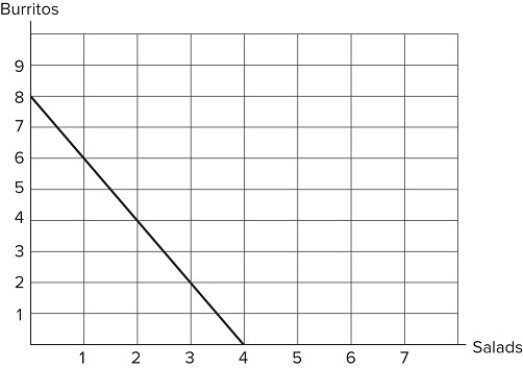 If the graph shown represents Damien's budget constraint, what can be said about burritos?
If the graph shown represents Damien's budget constraint, what can be said about burritos?
A) Burritos cost twice as much as salads.
B) Burritos cost half as much as salads.
C) Damien likes burritos more than salads.
D) Damien is willing to pay twice as much for burritos as he is for salads.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A budget constraint shows different bundles of goods that all:
A) yield the same total utility.
B) cost the same amount.
C) maximize an individual's utility.
D) maximize total utility at varying levels of income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The concept of utility can be used to explain why people are:I. charitable.II. altruistic.III. selfish.
A) III only
B) I and II only
C) None of these
D) I, II, and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A budget constraint is a line that is composed of:
A) all possible combinations of goods and services that maximize a consumer's total utility.
B) the additional utility gained from consuming all possible combinations of goods and services.
C) all possible combinations of goods and services that a consumer can buy with his or her income.
D) the total utility gained from consuming all possible combinations of goods and services with a certain income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If Bohai has one piece of gum in his mouth, he receives a utility of 12. If he puts a second piece of gum in his mouth, he will receive a marginal utility of 6. Adding a third piece will give a marginal utility of 1, and adding a fourth piece will cause Bohai to gag, yielding a marginal utility of -4. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Bob's total utility from chewing four pieces of gum would be 23.
B) Bob's total utility will decrease if he chews the fourth piece of gum.
C) Bob's total utility will be maximized if he eats two pieces of gum.
D) Bob's total utility will decrease after the first piece of gum.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Zachary spends his day off studying for a total of four hours and exercising for one hour. Using the concept of utility to explain his choices, which of the following is true?
A) The total utility he received from exercising for one hour was greater than the total utility he received from studying for four hours.
B) The marginal utility he received from exercising for the first hour was greater than the marginal utility he received from studying for the first hour.
C) The marginal utility he would have received from studying for a fifth hour would have been negative.
D) The marginal utility he would have received from studying for a fifth hour would have been less than the marginal utility he received from the first hour of exercise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The slope of a budget constraint:
A) represents the opportunity cost of the two goods relative to each other.
B) represents the relative marginal utilities from consuming the two goods.
C) measures the total utility the consumer gets from consuming the two goods.
D) is the consumer's income level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The substitution effect can be defined as the change in consumption that results from:
A) a change in the relative prices of goods.
B) increased effective wealth due to lower prices.
C) increased effective wealth due to increased income.
D) consumption change in income due to lower prices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rational utility maximizing consumers tend to:
A) buy the same bundle of goods regardless of the prices charged.
B) choose the same bundle of goods regardless of their income.
C) change their consumption choices when either prices or income changes.
D) change their consumption choices only when both prices and income change simultaneously.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
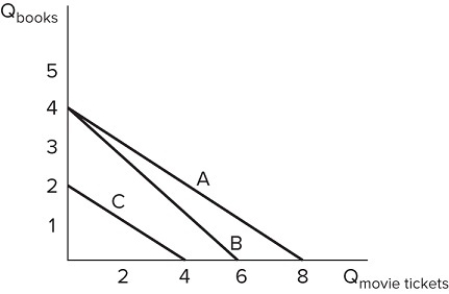 Assume Roger has $48 to spend on books and movie tickets and his budget constraint is represented by line B in the graph shown. What would cause his budget constraint to move to line A?
Assume Roger has $48 to spend on books and movie tickets and his budget constraint is represented by line B in the graph shown. What would cause his budget constraint to move to line A?
A) Roger gets a raise at work.
B) Roger gets unlimited coupons for $2 off the price of a movie ticket.
C) The price of movie tickets increases to $8.
D) None of these changes would cause Roger's budget constraint to move from line B to line A.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
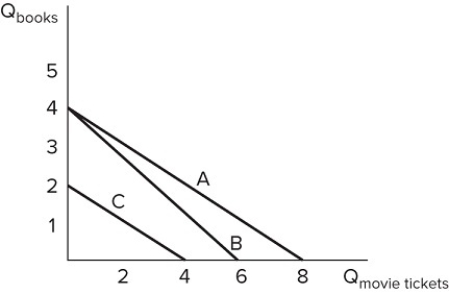 Suppose Bill has $48 to spend on the two items in the graph shown. If movie tickets cost $8, which line represents Bill's budget constraint?
Suppose Bill has $48 to spend on the two items in the graph shown. If movie tickets cost $8, which line represents Bill's budget constraint?
A) Line A
B) Line B
C) Line C
D) Either line A or B
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 140
Related Exams