Which of the following is true of the evolution of cell membranes?
A) Cell membranes have stopped evolving now that they are fluid mosaics.
B) Cell membranes cannot evolve if the membrane proteins do not.
C) The evolution of cell membranes is driven by the evolution of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
D) All components of membranes evolve in response to natural selection.
E) An individual organism selects its preferred type of cell membrane for particular functions.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Use the following information to answer the questions below.
The solutions in the two arms of this U-tube are separated by a membrane that is permeable to water and glucose but not to sucrose.Side A is half-filled with a solution of 2 M sucrose and 1 M glucose.Side B is half-filled with 1 M sucrose and 2 M glucose.Initially,the liquid levels on both sides are equal.
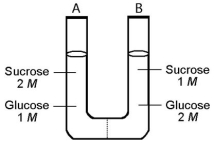 -After the system reaches equilibrium,what changes are observed?
-After the system reaches equilibrium,what changes are observed?
A) The molarity of sucrose and glucose are equal on both sides.
B) The molarity of glucose is higher in side A than in side B.
C) The water level is higher in side A than in side B.
D) The water level is unchanged.
E) The water level is higher in side B than in side A.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified