A) decrease the equilibrium quantity.
B) increase the equilibrium quantity.
C) have no effect on the equilibrium price.
D) decrease the equilibrium price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Figure: Market 4) Use the graph to answer the question.
The graph show the marginal social benefit, demand, and supply curves in the milkshake market. Market forces would yield a quantity of _____ and a price of _____ in the milkshake market.
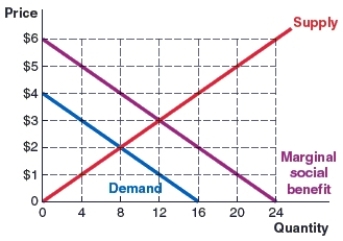
A) 12; $1
B) 16; $4
C) 12; $3
D) eight; $2
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The socially optimal amount of an externality is:
A) zero.
B) one-half of the amount of the externality that the market would produce.
C) based on cost-benefit analysis.
D) the amount that market forces would produce.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In general, a corrective subsidy:
A) will fail in the presence of negative externalities.
B) will yield the same result as a corrective tax.
C) will result in a socially optimal outcome when MSB> MSC.
D) can lead to a socially optimal outcome.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply curve of a firm is also its _____ cost curve.
A) average
B) social
C) marginal private
D) marginal external
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cap and trade is a system of:
A) subsidies used to internalize pollution costs.
B) taxes in which consumers are charged for the use of common property resources.
C) limits on allowable emissions.
D) exchangeable licenses that enable a holder to pollute up to a specified amount during a given period.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is a private good?
A) a police officer directing traffic
B) hiking trails in a national forest
C) a Wendy's hamburger
D) free Wi-Fi in an internet hotspot
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Figure: A Competitive Market in the Presence of Externalities) Use Figure: A Competitive Market in the Presence of Externalities. Given the figure, if there are no external benefits or costs, the output at Q will be:
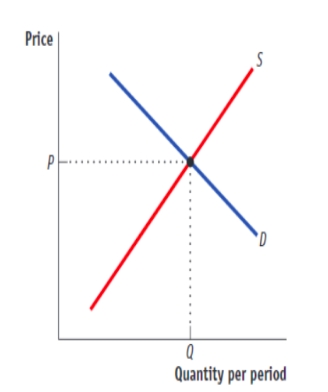
A) larger than is socially desirable.
B) smaller than is socially desirable.
C) socially optimum.
D) inefficient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement illustrates an environmental policy that uses cap and trade?
A) a levy on drivers of $0.25 per a set level of emissions
B) paying drivers $0.20 for each 15% reduction in driving emissions
C) allowing drivers to buy and sell rights to emit specified levels of vehicle emissions
D) ignoring pollution and letting private markets operate without government interference
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The benefit enjoyed by a buyer as a result of purchasing one additional unit of a good is the marginal _____ benefit.
A) external
B) social
C) personal
D) private
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
City police services and clean water are similar in that both are _____, but they differ in that clean water is _____, while city police services are not.
A) rival in consumption; excludable
B) nonrival in consumption; excludable
C) excludable; rival in consumption
D) nonexcludable; rival in consumption
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your college roommate has the right to practice her tuba during the day. You, however, find that studying during the day is most conducive to good grades, and her tuba-playing makes it difficult for you to concentrate. You make a deal with your roommate: you will clean the dorm room once a week if she will practice her tuba at other times or elsewhere. This is an example of
A) emission permits.
B) a corrective tax.
C) a corrective subsidy.
D) the Coase theorem.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would be both nonrival and nonexcludable?
A) a museum
B) a siren tornado warning system
C) a road
D) an immunization
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A good has a free-rider problem when:
A) any seller provides it for free as a special promotion.
B) someone can enjoy the benefits of the good without bearing the costs.
C) it can be transported at no cost to the consumer, with sellers bearing all transportation costs.
D) it has no negative externalities but only positive externalities.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens in a supply and demand diagram of the pesticide market when a corrective tax is used to solve a negative externality problem?
A) The equilibrium quantity rises as the supply curve shifts left.
B) The tax causes a rightward shift of the supply curve.
C) The marginal social cost curve becomes the supply curve.
D) The marginal external cost curve becomes the supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which good is MOST likely to be a public good?
A) Amazon Prime movie rental
B) a Six Flags amusement park
C) a pair of shoes
D) national defense
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An external benefit is:
A) a benefit enjoyed by the buyer of a good.
B) the total benefit to society of a good being consumed.
C) the benefit that the buyer receives from consuming a good outside of a market.
D) a benefit accruing to bystanders.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Figure: Market 2) Use the graph to answer the question.
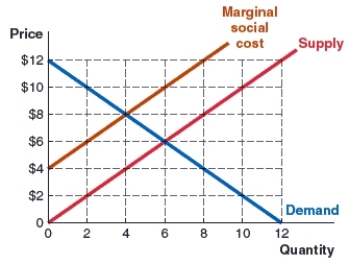
The graph shows the marginal social cost, demand, and supply curves in the cinnamon roll market. A corrective tax of _____ per unit will move the cinnamon roll market to the socially optimal output of _____ units.
The graph shows the marginal social cost, demand, and supply curves in the cinnamon roll market. A corrective tax of _____ per unit will move the cinnamon roll market to the socially optimal output of _____ units.
A) $4; 4
B) $8; 4
C) $6; 6
D) $2; 6
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the city of Cleveland has set an emissions tax to reduce the amount of pollution going into the Cuyahoga River. Assume that the optimal tax would be $2,500 but that city officials have set the tax at $1,000. At the equilibrium with the $1,000 tax:
A) there will be too much pollution.
B) the marginal social cost of pollution will be less than $1,000.
C) the marginal social benefit of pollution will be less than $1,000.
D) the marginal social benefit of pollution will be more than $1,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A public good, such as national defense, _____ excludable and is _____ in consumption.
A) is; rival
B) is; nonrival
C) is not; rival
D) is not; nonrival
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 241
Related Exams