A) is a silent mutation
B) is a nonsense mutation
C) usually has no effect on the function of the protein
D) is a missense mutation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How are RNA hairpin turns related to termination?
A) The turns are formed from complementary base pairing and cause separation of the RNA transcript and RNA polymerase.
B) A three-base repeat signals a stop sequence,and the RNA transcript is released.
C) Release factors bind to sites on the hairpin turn,causing release of the RNA transcript.
D) The hairpin turn prevents more nucleoside triphosphates from entering the active site of the enzymes,effectively shutting off the process of polymerization.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What molecule/feature ensures that the correct amino acid is added with reading of a specific codon during translation?
A) the anticodon of a properly formed aminoacyl tRNA
B) the methyl-guanosine cap of a properly modified mRNA
C) the poly (A) tail of a properly modified mRNA
D) the twisting number of a properly supercoiled DNA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16.2.
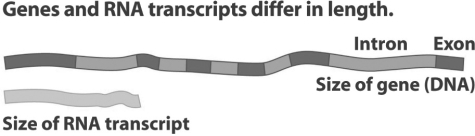 -Refer to Figure 16.2.The mRNA is smaller than the length of the DNA that codes for it because _____.
-Refer to Figure 16.2.The mRNA is smaller than the length of the DNA that codes for it because _____.
A) the regulatory regions (introns) of the gene are not transcribed
B) post-transcriptional modification removes the introns
C) post-transcriptional modification removes the exons
D) bases are added to the tail of the primary transcript
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16.3.
 -Refer to Figure 16.3.What is the function of the AGU on the loop of the tRNA?
-Refer to Figure 16.3.What is the function of the AGU on the loop of the tRNA?
A) It attaches to the amino acid.
B) It base pairs with the codon of mRNA.
C) It stabilizes the tRNA-amino acid complex.
D) It is the active site of this ribozyme.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following occurs in prokaryotes,but not eukaryotes?
A) post-transcriptional splicing
B) concurrent transcription and translation
C) translation in the absence of a ribosome
D) gene regulation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the DNA code for a particular amino acid is AGT,then the anticodon on the tRNA would be _____.
A) AGT
B) TCA
C) UCA
D) AGU
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not occur in post-transcriptional modifications occurring in eukaryotic mRNAs?
A) addition of a poly (A) tail
B) addition of a methyl-guanosine cap
C) removal of introns
D) RNA polymerase termination
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alpha-amanitin is a toxin produced by the death cap mushroom.It blocks the synthesis of mRNA.What effect would it have on health of the organism that ate death cap mushrooms?
A) It would block DNA synthesis.
B) It would tie up Mg²⁺ and through this action,inhibit glycolysis.
C) It would denature existing proteins.
D) It would cause death.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does termination of translation take place?
A) The end of the mRNA molecule is reached.
B) A stop codon is reached.
C) The 5' cap is reached.
D) The poly A tail is reached.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There should be a strong positive correlation between the rate of protein synthesis and _____.
A) the quantity of DNA polymerase
B) the quantity of RNA polymerase
C) the size of mRNA
D) the number of ribosomes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Codons are three-base sequences that specify the addition of a single amino acid.How do eukaryotic codons and prokaryotic codons compare?
A) Prokaryotic codons usually contain different bases than those of eukaryotes.
B) Prokaryotic codons usually specify different amino acids than those of eukaryotes.
C) The translation of codons is mediated by tRNAs in eukaryotes,but translation requires no intermediate molecules such as tRNAs in prokaryotes.
D) Codons are a nearly universal language among all organisms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Eukaryotes have three nuclear RNA polymerases.The primary function of RNA polymerase II is _____.
A) transcription of only rRNA-coding genes
B) transcription of only tRNA-coding genes
C) transcription of both rRNA- and tRNA-coding genes
D) transcription of protein-coding genes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ribosome-binding site of prokaryotes is also known as _____.
A) the TATA box
B) the promoter
C) the Shine-Dalgarno sequence
D) the Pribnow box
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16.1
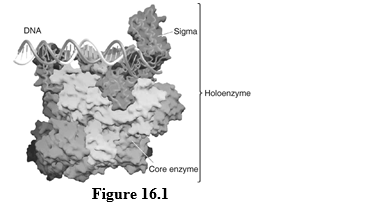 -The enzyme complex associated with DNA in the figure is _____.
-The enzyme complex associated with DNA in the figure is _____.
A) helicase
B) DNA polymerase
C) RNA polymerase
D) topoisomerase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are 61 codons that each specify the addition of a specific amino acid,and three stop codons for which there is no corresponding amino acid.However,there are only about 40 tRNA molecules,representing 40 anticodons.How is that possible?
A) Only about 40 of the recognized 61 codons are present in mRNA.
B) An anticodon forms hydrogen bonds with the codon;it must match the first two bases of the codon,but is less specific with respect to the third base.
C) There are tRNAs that can bind one of two related amino acids.
D) Only 20 of the codons are active-one for each amino acid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes is central to the initiation of transcription?
A) binding of sigma to the promoter region
B) formation of a phosphodiester bond in the elongating RNA strand
C) binding of DNA polymerase to the promoter region
D) formation of a DNA primer
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What molecule in the spliceosome lowers the activation energy so intron removal reactions can occur?
A) RNA polymerase
B) ribozymes
C) proteins of the spliceosome
D) autocatalysis by introns
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 38 of 38
Related Exams