A) the number of firms in the market.
B) the ease with which firms can enter and exit the market.
C) the ability of firms to differentiate their product.
D) All of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price floors and price ceilings
A) always reduce total surplus.
B) reduce consumer surplus and increase producer surplus.
C) reduce producer surplus and increase consumer surplus.
D) Not enough information to determine.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Producer surplus equals
A) total revenue minus total variable cost.
B) total revenue minus the sum of all marginal cost.
C) profit plus fixed cost.
D) All of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deadweight loss occurs when
A) consumer surplus is greater than producer surplus.
B) surplus losses to one group due to intervention are not offset by surplus gains to another.
C) consumer surplus is reduced.
D) consumer surplus is negative.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
As the quantity produced of a good increases, the social welfare generated by that good increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run, firms in a competitive market
A) shut down because profit goes to zero.
B) lose money.
C) are not profit maximizing.
D) earn zero economic profit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about profit maximizing firms in a competitive market is FALSE?
A) Firms earn no economic profit in the long run.
B) Marginal revenue does not have to equal marginal cost.
C) p - MC = 0.
D) Price equals marginal revenue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a competitive market, if buyers did not know all the prices charged by the many firms
A) all firms still face horizontal demand curves.
B) firms sell a differentiated product.
C) demand curves can be downward sloping for some or all firms.
D) the number of firms will most likely decrease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Producer surplus is equal to
A) the area under the supply curve.
B) the difference between price and average cost for all units sold.
C) the difference between price and marginal cost for all units sold.
D) the firm's profit when fixed costs exist.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
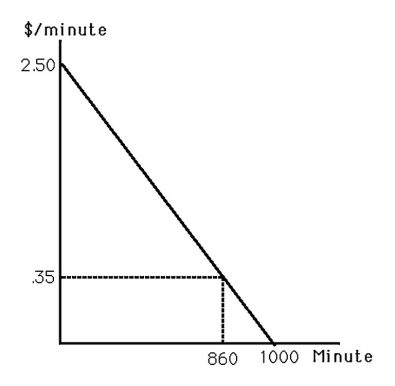 -The above figure shows the market demand curve for mobile telecommunications (time spent on a mobile phone) . At the current price of $0.35 per minute, consumer surplus equals
-The above figure shows the market demand curve for mobile telecommunications (time spent on a mobile phone) . At the current price of $0.35 per minute, consumer surplus equals
A) $301.00.
B) $924.50.
C) $1,225.50.
D) $1,250.00.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the absence of any government regulation on price, if a firm has no power to set price on its own, one can safely conclude
A) the demand curve for the firm's product is horizontal.
B) there aren't many firms in the industry.
C) the market is in long-run equilibrium.
D) the firms in this industry are not profitable.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between producer surplus and profit is always the associated
A) opportunity costs.
B) total costs.
C) variable costs.
D) fixed costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consumers seek to
A) maximize profits.
B) maximize expected consumer surplus.
C) maximize expenditures.
D) maximize choice.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consumer surplus
A) is the difference between what a consumer pays for a good and the producer's cost.
B) is the extra money a consumer pays above the minimum necessary price for the producer to produce it.
C) is the difference between what a consumer would willingly pay for a good and the price actually paid.
D) equals zero in the long run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a market is NOT perfectly competitive, then government intervention
A) is always justifiable.
B) will usually decrease economic well-being.
C) guarantees that societal well-being will be maximized.
D) may increase economic well-being.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assuming a horizontal long-run market supply curve, which of the following statements is (are) TRUE about competitive firms in the long run?
A) p = MC
B) p = AC
C) profit = 0
D) All of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Government intervention in a perfectly competitive market
A) reduces economic well-being.
B) is an illustration of the "invisible hand theorem."
C) increases economic well-being.
D) guarantees maximized well-being.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 97 of 97
Related Exams