The following questions are based on the reaction A + B → C + D shown in Figure 8.2.
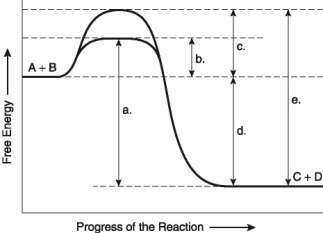 -How does a noncompetitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme reaction?
-How does a noncompetitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme reaction?
A) by binding at the active site of the enzyme
B) by changing the shape of a reactant
C) by changing the free energy change of the reaction
D) by acting as a coenzyme for the reaction
E) by decreasing the activation energy of the reaction
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
When 10,000 molecules of ATP are hydrolyzed to ADP and Pi in a test tube, about twice as much heat is liberated as when a cell hydrolyzes the same amount of ATP. Which of the following is the best explanation for this observation?
A) Cells are open systems, but a test tube is a closed system.
B) Cells are less efficient at heat production than nonliving systems.
C) The hydrolysis of ATP in a cell produces different chemical products than does the reaction in a test tube.
D) The reaction in cells must be catalyzed by enzymes, but the reaction in a test tube does not need enzymes.
E) Reactant and product concentrations are not the same
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified