A) State and local governments cannot default on their bonds.
B) Bonds issued by state and local governments are called municipal bonds.
C) All government issued bonds - local, state, and federal - are federal income tax exempt.
D) The coupon payment on municipal bonds is usually higher than the coupon payment on Treasury bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If 1-year interest rates for the next five years are expected to be 4,2,5,4,and 5 percent,and the 5-year term premium is 1 percent,than the 5-year bond rate will be
A) 2 percent.
B) 3 percent.
C) 4 percent.
D) 5 percent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the yield curve slope is flat for short maturities and then slopes steeply upward for longer maturities,the liquidity premium theory (assuming a mild preference for shorter-term bonds) indicates that the market is predicting
A) a rise in short-term interest rates in the near future and a decline further out in the future.
B) constant short-term interest rates in the near future and further out in the future.
C) a decline in short-term interest rates in the near future and a rise further out in the future.
D) constant short-term interest rates in the near future and a decline further out in the future.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the expected path of 1-year interest rates over the next five years is 2 percent,4 percent,1 percent,4 percent,and 3 percent,the expectations theory predicts that the bond with the lowest interest rate today is the one with a maturity of
A) one year.
B) two years.
C) three years.
D) four years.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in the liquidity of corporate bonds will ________ the price of corporate bonds and ________ the yield of Treasury bonds,everything else held constant.
A) increase; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; decrease
D) decrease; increase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A plot of the interest rates on default-free government bonds with different terms to maturity is called
A) a risk-structure curve.
B) a default-free curve.
C) a yield curve.
D) an interest-rate curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
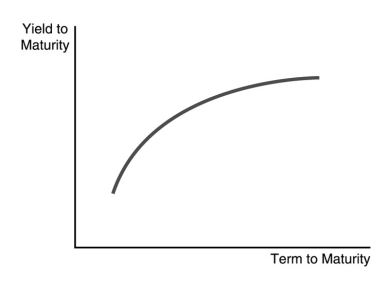 -The steeply upward sloping yield curve in the figure above indicates that ________ interest rates are expected to ________ in the future.
-The steeply upward sloping yield curve in the figure above indicates that ________ interest rates are expected to ________ in the future.
A) short-term; rise
B) short-term; fall moderately
C) short-term; remain unchanged
D) long-term; fall moderately
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the probability of a bond default increases because corporations begin to suffer large losses,then the default risk on corporate bonds will ________ and the expected return on these bonds will ________,everything else held constant.
A) decrease; increase
B) decrease; decrease
C) increase; increase
D) increase; decrease
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A(n) ________ in the liquidity of corporate bonds will ________ the price of corporate bonds and ________ the yield on corporate bonds,all else equal.
A) increase; increase; decrease
B) increase; decrease; decrease
C) decrease; increase; increase
D) decrease; decrease; decrease
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the liquidity premium theory of the term structure,a steeply upward sloping yield curve indicates that short-term interest rates are expected to
A) rise in the future.
B) remain unchanged in the future.
C) decline moderately in the future.
D) decline sharply in the future.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the liquidity premium theory,a yield curve that is flat means that
A) bond purchasers expect interest rates to rise in the future.
B) bond purchasers expect interest rates to stay the same.
C) bond purchasers expect interest rates to fall in the future.
D) the yield curve has nothing to do with expectations of bond purchasers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bond with default risk will always have a ________ risk premium and an increase in its default risk will ________ the risk premium.
A) positive; raise
B) positive; lower
C) negative; raise
D) negative; lower
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following long-term bonds has the highest interest rate?
A) Corporate Baa bonds
B) U.S. Treasury bonds
C) Corporate Aaa bonds
D) Municipal bonds
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in default risk on corporate bonds ________ the demand for these bonds,but ________ the demand for default-free bonds,everything else held constant.
A) increases; lowers
B) lowers; increases
C) does not change; greatly increases
D) moderately lowers; does not change
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Typically,yield curves are
A) gently upward sloping.
B) mound shaped.
C) flat.
D) bowl shaped.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bonds with no default risk are called
A) flower bonds.
B) no-risk bonds.
C) default-free bonds.
D) zero-risk bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following securities has the lowest interest rate?
A) Junk bonds
B) U.S. Treasury bonds
C) Investment-grade bonds
D) Corporate Baa bonds
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the liquidity premium theory of the term structure,a flat yield curve indicates that short-term interest rates are expected to
A) rise in the future.
B) remain unchanged in the future.
C) decline moderately in the future.
D) decline sharply in the future.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When yield curves are downward sloping,
A) long-term interest rates are above short-term interest rates.
B) short-term interest rates are above long-term interest rates.
C) short-term interest rates are about the same as long-term interest rates.
D) medium-term interest rates are above both short-term and long-term interest rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a corporation begins to suffer large losses,then the default risk on the corporate bond will
A) increase and the bond's return will become more uncertain, meaning the expected return on the corporate bond will fall.
B) increase and the bond's return will become less uncertain, meaning the expected return on the corporate bond will fall.
C) decrease and the bond's return will become less uncertain, meaning the expected return on the corporate bond will fall.
D) decrease and the bond's return will become less uncertain, meaning the expected return on the corporate bond will rise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 113
Related Exams