A) kidneys.
B) pancreas.
C) adrenal gland.
D) posterior pituitary gland.
E) anterior pituitary gland.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a positive-feedback system in which hormone A alters the amount of protein X
A) an increase in A always produces an increase in X.
B) an increase in X always produces a decrease in A.
C) a decrease in A always produces an increase in X.
D) a decrease in X always causes a decrease in A.
E) it is impossible to predict how A and X affect each other.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The higher level of metabolic activity typical of nonhibernating temperate mammals during the winter months is due to increased secretion of
A) ecdysteroid.
B) glucagon.
C) thyroxine.
D) oxytocin.
E) growth hormone.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a person loses a large amount of water in a short period of time, he or she may die from dehydration. ADH can help reduce water loss through its interaction with its target cells in the
A) anterior pituitary.
B) posterior pituitary.
C) adrenal gland.
D) bladder.
E) kidney.
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
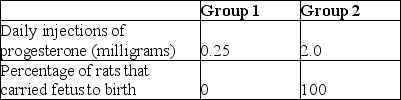 In an experiment, rats' ovaries were removed immediately after impregnation and then the rats were divided into two groups. Treatments and results are summarized in the table. The results most likely occurred because progesterone exerts an effect on the
In an experiment, rats' ovaries were removed immediately after impregnation and then the rats were divided into two groups. Treatments and results are summarized in the table. The results most likely occurred because progesterone exerts an effect on the
A) general health of the rat.
B) size of the fetus.
C) metabolism of the uterus.
D) gestation period of rats.
E) number of eggs fertilized.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell with membrane-bound proteins that selectively bind a specific hormone is called that hormone's
A) secretory cell.
B) plasma cell.
C) endocrine cell.
D) target cell.
E) regulatory cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A disease that destroys the adrenal cortex should lead to an increase in the plasma levels of
A) glucocorticoid hormones.
B) epinephrine.
C) adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) .
D) glucose.
E) acetylcholine.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Linkage to membrane-bound receptor proteins on target cells activates the typical actions of the
A) androgens.
B) glucocorticoids.
C) estrogens.
D) pancreatic hormones.
E) progestins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relationship between the insect hormones ecdysteroid and PTTH is an example of
A) an interaction of the endocrine and nervous systems.
B) homeostasis achieved by positive feedback.
C) how peptide-derived hormones have more widespread effects than steroid hormones.
D) homeostasis maintained by antagonistic hormones.
E) competitive inhibition of a hormone receptor.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DES is called an "endocrine disrupting chemical" because it structurally resembles, and interferes with, the endocrine secretions of the
A) pancreatic islet cells.
B) thyroid gland.
C) adrenal medulla.
D) ovaries.
E) hypothalamus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reason that the steroid hormone aldosterone affects only a small number of cells in the body is that
A) only its target cells get exposed to aldosterone.
B) only its target cells contain aldosterone receptors.
C) it is unable to enter nontarget cells.
D) nontarget cells destroy aldosterone before it can produce any effect.
E) nontarget cells convert aldosterone to a hormone to which they do respond.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which hormone is incorrectly paired with its action?
A) oxytocin - stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth
B) thyroxine - stimulates metabolic processes
C) insulin - stimulates glycogen breakdown in the liver
D) ACTH - stimulates the release of glucocorticoids by the adrenal cortex
E) melatonin - affects biological rhythms, seasonal reproduction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prostaglandins are local regulators whose chemical structure is derived from
A) oligosaccharides.
B) fatty acids.
C) steroids.
D) amino acids.
E) nitric oxide.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Melatonin is secreted by
A) the hypothalamus during the day.
B) the pineal gland during the night.
C) the autonomic nervous system during the winter.
D) the posterior pituitary gland during the day.
E) the thyroid gland during cold seasons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has both endocrine and exocrine activity?
A) the pituitary gland
B) parathyroid glands
C) salivary glands
D) the pancreas
E) adrenal glands
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After eating a carbohydrate-rich meal, the mammalian pancreas increases its secretion of
A) ecdysteroid.
B) glucagon.
C) thyroxine.
D) oxytocin.
E) insulin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the next few questions. Your niece is playing in the backyard and finds a beautiful moth. Being interested in insects, you perform research to find out what kind of moth it is. You determine that it is a luna moth (Actias luna) . Similar to other moths, the luna moth moults several times throughout development and ultimately metamorphoses into a mouthless adult. The adult will live for approximately one week with the sole purpose of mating. -In order to attract a mate, female luna moths secrete
A) mucus.
B) pheromones.
C) neurotransmitters.
D) cytokines.
E) ecdysteroid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following functions of prolactin are incorrectly paired with the species?
A) stimulate mammary gland growth - reptiles
B) milk synthesis - mammals
C) regulate NaCl and H₂O balance - freshwater fishes
D) metamorphosis delay - amphibians
E) fat metabolism - birds
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a lactating mammal, the two hormones that promote milk synthesis and milk release, respectively, are
A) prolactin and calcitonin.
B) prolactin and oxytocin.
C) follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone.
D) luteinizing hormone and oxytocin.
E) prolactin and luteinizing hormone.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A paracrine signal that relaxes smooth muscle cells is
A) nitric oxide.
B) vitamin D.
C) testosterone.
D) cortisol.
E) antidiuretic hormone.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 82
Related Exams