A) trial-and-error learning plus habituation.
B) trial-and-error learning plus social learning.
C) trial-and-error learning plus imprinting.
D) habituation plus social learning.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of agonistic behavior?
A) A dog raises its hackles, bares its teeth, and stands tall to appear threatening.
B) A honeybee does a waggle dance to indicate the direction of food.
C) A male ruffed grouse spreads its tail and beats its wings to attract a female.
D) Ants mark their trails by releasing pheromones.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a nipple is placed in a newborn baby's mouth, the infant will immediately begin to suckle. This is an example of
A) imprinted behavior.
B) classical conditioning.
C) innate behavior.
D) imitation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cross-fostering experiments with Norway rat pups showed that in their response to stress,
A) environment was the critical factor, not genetics.
B) genetics was the only important factor.
C) both genetics and the environment played a clear role.
D) cross-fostered pups resembled their biological mothers more than their foster mothers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are told that the song of males among a particular songbird species has an innate component but is also largely learned. Nestling males imprint on their father's song and then sing it themselves when they reach sexual maturity. Which of the following observations would lead you to doubt this information?
A) A male chick reared in isolation but introduced as an older juvenile into an aviary containing normal males of his species sings his species' song.
B) A male chick who is reared in isolation but hears tape recordings of his species' song grows up to sing normally.
C) A male chick who is reared in isolation but hears tape recordings of a different species' song grows up to sing that species' song.
D) A male chick fostered in the nest of a different species grows up to sing the song of its foster species.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After reading the paragraph below, answer the questions that follow.
In examining the effects of atrazine, one of the most commonly used herbicides in the world, scientists studied the mating behavior of male frogs exposed to atrazine (Atr) compared to a group that was not exposed (Non) . The results are shown in the figure.
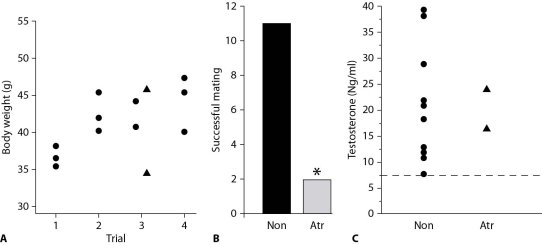 -Part B indicates that
-Part B indicates that
A) atrazine is an endocrine disrupter.
B) trazine-treated males are more successful in mating than nontreated males.
C) there were fewer atrazine-treated males than nontreated males.
D) atrazine males are unable to mate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sending of, reception of, and response to signals constitute animal
A) cost-benefit analysis.
B) communication.
C) problem solving.
D) associative learning.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In some social insects, there are individuals that do not mate or may not be fertile but help look after other members of their group. Which statement regarding this situation is true?
A) There is no way that natural selection can act on the genes of nonreproducers since they do not leave offspring.
B) The ultimate cause of this behavior is the need to keep their group safe.
C) By protecting relatives, the nonreproducers increase the probability that their genes will be passed to the next generation.
D) Lack of mating is an agonistic behavior.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many rats were tested for their ability to learn to navigate a maze. The average number of errors, for a total of 14 trials, was 64 per rat. The rats that made the fewest errors were bred to each other, and the offspring were tested in a similar way. This process was repeated for seven generations, at which point the average number of errors for 14 trials was 36. This experiment demonstrates that
A) learned behavior cannot be inherited.
B) maze-learning ability has a genetic basis.
C) maze-learning ability depends mainly on early contact with adept parents.
D) natural selection has a role in the evolution of fixed action patterns but not in the evolution of behavior involving learning.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following situations represents an example of territorial behavior?
A) Digger wasps are able to recognize the pattern of landmarks around their nests.
B) Sow bugs become more active and move around randomly if they find themselves in a dry area.
C) Gannets breed in dense colonies. Each gannet defends the area within the beak's reach of its nest, but gannets feeding at sea are indifferent to each other.
D) Troops of monkey species use well-defined, widely overlapping ranges. Troops avoid encountering each other and are aggressive if they meet.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following conclusions is supported by this graph? 
A) Prey size does not affect the number of calories gained per second of handling time by wagtails.
B) Wagtails get more calories per second of handling time with larger flies than with smaller ones.
C) Wagtails get more calories per second of handling time with smaller flies than with larger ones.
D) Wagtails get more calories per second of handling time with 7-mm flies than with either larger or smaller ones.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From a sociobiological perspective, altruism is a behavior that
A) does not have a genetic basis.
B) has the potential to enhance the altruist's fitness at a later point in time.
C) will always be selected against.
D) occurs only in the social insects.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 52 of 52
Related Exams