A) when heart rate is slow
B) when heart rate is fast
C) when the force of contraction is decreased
D) when the difference between the end diastolic volume and the end systolic volume is small
E) when calcium channel blockers are present
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the Frank-Starling principle,the cardiac output is directly related to (the)
A) size of the ventricle.
B) heart rate.
C) venous return.
D) thickness of the myocardium.
E) total amount of blood in the cardiovascular system.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A faster-than-normal heart rate is called
A) bradycardia.
B) tachycardia.
C) tetanus.
D) myocardial infarct.
E) arrhythmia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ permit the exchange of nutrients,dissolved gases,and waste products between the blood and surrounding tissues.
A) Veins
B) Arteries
C) Arterial trunks
D) Capillaries
E) Vena cavae
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following indicates the start of the systemic circuit?
A) pulmonary trunk
B) pulmonary arteries
C) vena cavae
D) ascending aorta
E) cardiac veins
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cardiac muscle cells have abundant reserves of myoglobin,which function in
A) removing waste products.
B) storing iron.
C) removing carbon dioxide.
D) storing oxygen.
E) the shortening of individual sarcomeres.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a decline in blood pressure or oxygen concentrations occurs,the cardiac centers then call for a(n)
A) decrease in cardiac output.
B) decrease in sympathetic motor neuron activity.
C) decrease in stroke volume.
D) increase in parasympathetic motor neuron activity.
E) increase in cardiac output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Explain the significance of the thickness of the left ventricular wall.
Correct Answer

verified
The thicker wall of the left ventricle a...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
The QRS complex on an ECG tracing represents
A) atrial depolarization.
B) atrial repolarization.
C) ventricular depolarization.
D) ventricular repolarization.
E) ventricular contraction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The muscle layer of the heart is the
A) epicardium.
B) myocardium.
C) endocardium.
D) visceral pericardium.
E) endothelium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Veins that return blood to the heart are also referred to as ________ vessels.
A) afferent
B) mitral
C) valvular
D) efferent
E) pulmonary
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During repolarization,________ ions rush out of the ventricular contractile cell.
A) sodium
B) calcium
C) magnesium
D) selenium
E) potassium
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The maximum rate of contraction in normal cardiac muscle fibers is approximately ________ per minute.
A) 80
B) 140
C) 200
D) 250
E) 300+
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
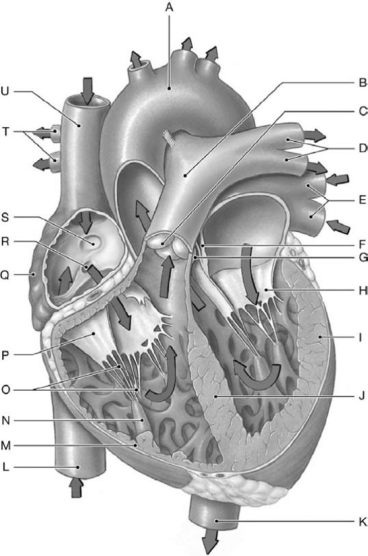 Figure 12-1 Major Internal Landmarks of the Heart
Use Figure 12-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label N represents the
Figure 12-1 Major Internal Landmarks of the Heart
Use Figure 12-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label N represents the
A) trabeculae carneae.
B) chordae tendineae.
C) auricle.
D) papillary muscle.
E) pectinate muscle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 12-1 Major Internal Landmarks of the Heart
Use Figure 12-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label K represents the
Figure 12-1 Major Internal Landmarks of the Heart
Use Figure 12-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label K represents the
A) aortic arch.
B) pulmonary trunk.
C) descending aorta.
D) superior vena cava.
E) inferior vena cava.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pulmonary arteries carry blood to the
A) heart.
B) lungs.
C) brain.
D) kidneys.
E) pancreas.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following is a list of vessels and structures that are associated with the heart. 1.right atrium 2) left atrium 3) right ventricle 4) left ventricle 5) vena cavae 6) aorta 7) pulmonary trunk 8) pulmonary veins What is the correct order for the flow of blood entering from the systemic circulation?
A) 1, 2, 7, 8, 3, 4, 6, 5
B) 1, 7, 3, 8, 2, 4, 6, 5
C) 5, 1, 3, 7, 8, 2, 4, 6
D) 5, 3, 1, 7, 8, 4, 2, 6
E) 5, 1, 3, 8, 7, 2, 4, 6
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 12-1 Major Internal Landmarks of the Heart
Use Figure 12-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label S represents the
Figure 12-1 Major Internal Landmarks of the Heart
Use Figure 12-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label S represents the
A) interventricular septum.
B) apex.
C) opening of the coronary sinus.
D) fossa ovalis.
E) interatrial septum.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is correct regarding the heart wall?
A) The endothelium consists of cardiac muscle tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
B) The myocardium is comprised of a simple squamous epithelium and an underlying layer of areolar tissue.
C) The endocardium is the visceral pericardium.
D) The cardiac muscle tissue forms bands that wrap around the ventricles and spiral into the wall of the atria.
E) The epicardium is a serous membrane that consists of an exposed epithelium and an underlying layer of areolar tissue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The semilunar valves prevent backflow into the
A) atria.
B) aorta.
C) ventricles.
D) pulmonary trunk.
E) venae cavae.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 115
Related Exams