A) Sam continues to smoke because he has a right to smoke in the smoking section.
B) Charles offers Sam between $15 and $40 not to smoke.Sam accepts,and both parties are better off.
C) Charles offers Sam between $15 and $40 not to smoke.Sam declines because he has a right to smoke in the smoking section.
D) Only a government policy banning smoking in restaurants will solve this problem.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a negative externality exists in a market,the cost to producers
A) is greater than the cost to society.
B) will be the same as the cost to society.
C) will be less than the cost to society.
D) will differ from the cost to society,regardless of whether an externality is present.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Coase theorem states that
A) taxes are an efficient way for governments to remedy negative externalities.
B) subsidies are an efficient way for governments to remedy positive externalities.
C) industrial policies encourage technology spillovers.
D) in the absence of transaction costs,private parties can solve the problem of externalities on their own.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A negative externality will cause a private market to produce
A) less than is socially desirable.
B) more than is socially desirable.
C) exactly the quantity that is socially desirable.
D) less than the same market would produce in the presence of a positive externality.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that elementary education creates a positive externality.If the government subsidizes education by an amount equal to the per-unit externality it creates,then
A) the equilibrium quantity of education will equal the socially optimal quantity of education.
B) the equilibrium quantity of education will be greater than the socially optimal quantity of education.
C) the equilibrium quantity of education will be less than the socially optimal quantity of education.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
University researchers create a positive externality because what they discover in their research labs can easily be learned by others who haven't contributed to the research costs.If there are no subsidies,what is the relationship between the equilibrium quantity of university research and the optimal quantity of university research produced?
A) They are equal.
B) The equilibrium quantity is greater than the socially optimal quantity.
C) The equilibrium quantity is less than the socially optimal quantity.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) Tradable pollution permits have an advantage over corrective taxes if the government is uncertain as to the optimal size of the tax necessary to reduce pollution to a specific level.
B) Both corrective taxes and tradable pollution permits provide market-based incentives for firms to reduce pollution.
C) Corrective taxes set the maximum quantity of pollution,whereas tradable pollution permits fix the price of pollution.
D) Both corrective taxes and tradable pollution permits reduce the cost of environmental protection and thus should increase the public's demand for a clean environment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-3 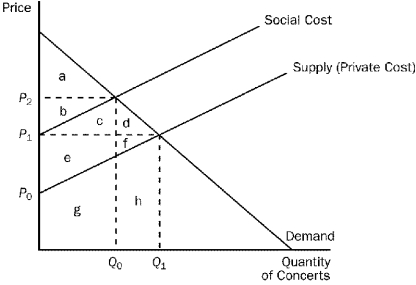 -Refer to Figure 10-3.The social cost curve is above the supply curve because
-Refer to Figure 10-3.The social cost curve is above the supply curve because
A) it takes into account the external costs imposed on society by the concert.
B) it takes into account the effect of local noise restrictions on concerts in parks surrounded by residential neighborhoods.
C) concert tickets are likely to cost more than the concert actually costs the organizers.
D) residents in the surrounding neighborhoods get to listen to the concert for free.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an advantage of corrective taxes?
A) They raise revenues for the government.
B) They enhance economic efficiency.
C) They subsidize the production of goods with positive externalities.
D) They move the allocation of resources closer to the social optimum.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-9 
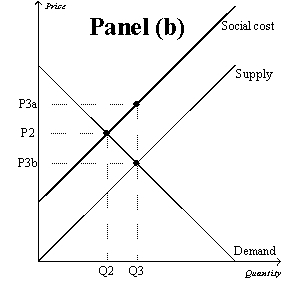
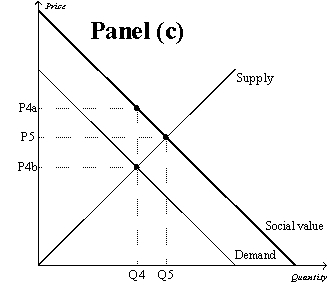 -Refer to Figure 10-9,Panel (b) and Panel (c) .The overuse of antibiotics leads to the development of antibiotic-resistant diseases.Therefore,a government policy that internalized the externality would move the quantity of antibiotics used from point
-Refer to Figure 10-9,Panel (b) and Panel (c) .The overuse of antibiotics leads to the development of antibiotic-resistant diseases.Therefore,a government policy that internalized the externality would move the quantity of antibiotics used from point
A) Q2 to point Q3.
B) Q3 to point Q2.
C) Q4 to point Q5.
D) Q5 to point Q4.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between social cost and private cost is a measure of the
A) loss in profit to the seller as the result of a negative externality.
B) cost of an externality.
C) cost reduction when the negative externality is eliminated.
D) cost incurred by the government when it intervenes in the market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
According to recent research,the gas tax in the United States is lower than the optimal level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Barking dogs cannot be considered an externality because externalities must be associated with some form of market exchange.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a characteristic of pollution permits?
A) Prices are set by supply and demand.
B) Allowing firms to trade their permits reduces the total quantity of pollution beyond the initial allocation.
C) Real-world markets for pollution permits include sulfur dioxide and carbon.
D) Firms for whom pollution reduction is very expensive are willing to pay more for permits than firms for whom pollution reduction is less expensive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An optimal tax on pollution would result in which of the following?
A) Producers will choose not to produce any pollution.
B) Producers will internalize the cost of the pollution.
C) Producers will maximize production.
D) The value to consumers at market equilibrium will exceed the social cost of production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An externality is an example of
A) a corrective tax.
B) a tradable pollution permit.
C) a market failure.
D) Both a and b are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Externalities can be corrected by each of the following except
A) self-interest.
B) moral codes and social sanctions.
C) charity.
D) normal market adjustments.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-1 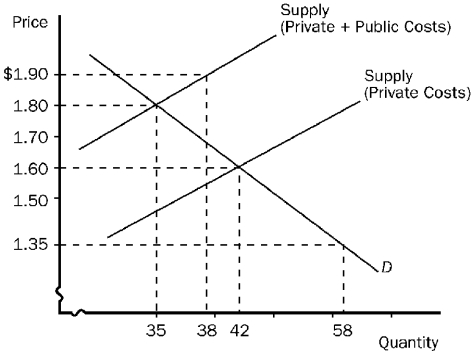 -Refer to Figure 10-1.This graph represents the tobacco industry.The socially optimal price and quantity are
-Refer to Figure 10-1.This graph represents the tobacco industry.The socially optimal price and quantity are
A) $1.90 and 38 units,respectively.
B) $1.80 and 35 units,respectively.
C) $1.60 and 42 units,respectively.
D) $1.35 and 58 units,respectively.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When negative externalities are present in a market,
A) producers will be affected but consumers will not.
B) producers will supply too much of the product.
C) demand will be too high.
D) the market will still maximize total benefits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-16 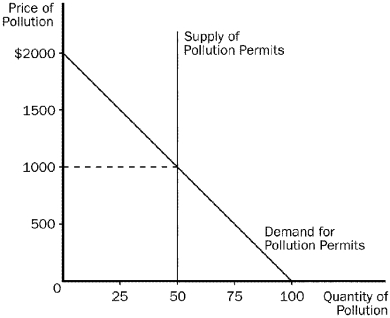 -Refer to Figure 10-16.This graph shows the market for pollution when permits are issued to firms and traded in the marketplace.The equilibrium number of permits is
-Refer to Figure 10-16.This graph shows the market for pollution when permits are issued to firms and traded in the marketplace.The equilibrium number of permits is
A) 50
B) 100
C) 1,000
D) 2,000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 439
Related Exams