A) entry by new firms.
B) economic profits by new firms.
C) economic profits for a few firms for a short time.
D) a leftward shift of the supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One difference between the long run and the short run in a perfectly competitive industry is that:
A) economic profits in the long run are always greater than they are in the short run.
B) economic profits in the short run are always greater than they are in the long run.
C) firms necessarily earn zero economic profit in the long run but may earn positive or negative economic profit in the short run.
D) firms necessarily earn positive economic profit in the long run but may earn positive or negative economic profit in the short run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The No Cash on the Table principle means unexploited opportunities:
A) never exist.
B) cannot be exploited for long.
C) can exist in equilibrium but rarely do.
D) always exist in equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an industry with free entry and exit,economic profits:
A) indicate a market failure.
B) can never occur.
C) provide incentives for a reallocation of resources out of other industries and into the one with economic profits.
D) can be sustained indefinitely.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Last year Pat was a soybean farmer and Chris was a corn farmer.This year,high demand for ethanol,an automobile fuel made from corn,causes the price of corn to increase. Refer to the information above.Suppose Pat stopped growing soybeans and began growing corn.What principle would explain that change?
A) The principle of comparative advantage.
B) The scarcity principle.
C) The incentive principle.
D) The equilibrium principle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Daily Supply and Demand: Oranges in Hurricane Alley 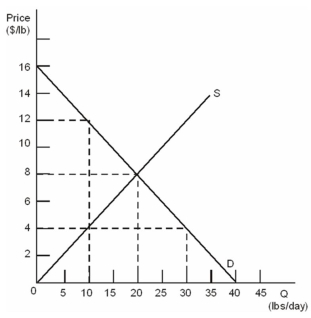 Refer to the figure above.What is the cost of harvesting the tenth pound of oranges?
Refer to the figure above.What is the cost of harvesting the tenth pound of oranges?
A) $2
B) $2.50
C) $4
D) $5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that all firms in this industry have identical cost functions. 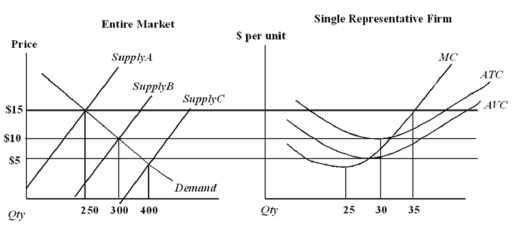 The firm depicted in the graph on the right faces a demand curve that
The firm depicted in the graph on the right faces a demand curve that
A) is horizontal at the market price.
B) is downward sloping,and less than market demand curve.
C) is the same as the marginal cost curve.
D) is the same as the market demand curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Explicit costs:
A) measure the opportunity costs of the business owners.
B) are always fixed in the short run.
C) measure the payments made to the firm's factors of production.
D) are always variable in the short run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the demand curve fails to capture all of the benefits of consumption,then the:
A) equilibrium price is efficient but the quantity will be too large.
B) the equilibrium price is inefficiently low.
C) government needs to impose regulations that require more consumption.
D) the equilibrium price is inefficiently high.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The statement,"price distributes goods and services to those that value them the most" refers to the ______ function of price.
A) allocative
B) multiplicative
C) store of value
D) rationing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sum of the economic surpluses accruing to buyers and sellers is:
A) producer surplus.
B) equal to profit.
C) total economics surplus.
D) consumer surplus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Last year Pat was a soybean farmer and Chris was a corn farmer.This year,high demand for ethanol,an automobile fuel made from corn,causes the price of corn to increase. Refer to the information above.You would predict that this year Pat may:
A) grow more soybeans.
B) switch to growing corn.
C) continue to grow the same amount of soybeans.
D) go out of business.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A price ceiling that is below the equilibrium price will cause:
A) producer surplus to fall.
B) total economic surplus to rise.
C) quantity supplied to exceed quantity demanded.
D) demand to increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which ordering best describes how a perfectly competitive industry would respond to a sudden increase in popularity of the product? The market demand function will shift to the right,causing the market:
A) price to increase,and a new stable equilibrium to be established at a higher price and higher quantity.
B) price to increase,and all firms in the industry will earn higher profits for the foreseeable future.
C) price to increase.Increased profits will encourage new firms to enter,shifting the market supply function to the right.Long-run market equilibrium will be at a higher quantity than before the surge in popularity.
D) price and quantity supplied to increase.Increased profits will encourage new firms to enter shifting the market supply function upward.Long-run market equilibrium will be at a lower quantity and higher price than before the surge in popularity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Professor Plum,who earns $75,000 per year,read in the paper today that the university pays its basketball coach one million dollars per year in exchange for the coach's agreement to remain at the university for at least three more years.The coach earns more than Professor Plum because:
A) demand for sporting events exceeds demand for college courses.
B) universities value sports over academics.
C) the coach is able to earn economic rent due to his unique talents.
D) the coach has more human capital than does Prof.Plum.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Accounting profits are:
A) equal to total revenues minus implicit costs.
B) the difference between total revenues and explicit costs.
C) equal to total revenues minus explicit and implicit costs.
D) less than economic profits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that in an effort to help single parents,the government has decided to pay part of the cost of childcare.This measure will
A) increase efficiency in the childcare market.
B) increase consumer surplus in the childcare market.
C) increase total surplus in the childcare market.
D) leave the quantity of childcare unchanged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ingrid has been waiting for the show "Mamma Mia!" to come to town.When it finally does come,ticket prices are $60.Ingrid's reservation price is $75.But when Ingrid tries to buy a ticket,they are sold out. Refer to the information above.Sven had purchased a ticket at the ticket window for $60.Sven's reservation price is $65.If Sven attends "Mamma Mia!" and Ingrid does not,it is:
A) inefficient because Sven and Ingrid could have made a mutually beneficial trade.
B) efficient because Sven paid less for the ticket than his reservation price.
C) efficient because Sven arrived at the ticket counter before the show was sold out.
D) inefficient because ticket prices are regulated by the government.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is always true that:
A) accounting profits are positive.
B) economic profits are zero.
C) economic profits are greater than or equal to accounting profits.
D) accounting profits greater than or equal to economic profits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If all firms in a perfectly competitive industry are experiencing economic losses,then firms will:
A) exit the industry,until economic profits are positive.
B) exit the industry,until accounting profits equal zero.
C) continue in the industry,hoping for better times.
D) exit the industry,until economic profits equal zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 115
Related Exams