A) productive efficiency and allocative efficiency.
B) monopoly power and ease of entry.
C) consumer choice and productive efficiency.
D) short-run profits and long-run efficiency.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Herfindahl index
A) tells us the degree to which monopolistically competitive firms are differentiating their products.
B) is another name for the four-firm concentration ratio.
C) tells us whether oligopolistic firms are engaging in collusion.
D) gives much greater weight to larger firms than to smaller firms in an industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that the short-run cost and demand data given in the tables below confront a monopolistic competitor selling a given product and engaged in a given amount of product promotion. If the firm sells 3 units of output, marginal revenue will be
A) -$5.
B) $35.
C) $135.
D) $165.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If some firms leave a monopolistically competitive industry, the demand curves of the remaining firms will
A) be unaffected.
B) shift to the left.
C) become more elastic.
D) shift to the right.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct?
A) The excess capacity problem diminishes as the monopolistically competitive firm's demand curve becomes less elastic.
B) The excess capacity problem means that monopolistically competitive firms typically produce at some point on the rising segment of their average total cost curve.
C) The greater the degree of product variation, the lesser is the excess capacity problem.
D) The greater the degree of product variation, the greater is the excess capacity problem.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which industry is monopolistic competition most likely to be found?
A) utilities
B) agriculture
C) retail trade
D) mining
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to a purely competitive firm in long-run equilibrium, the monopolistic competitor has a
A) lower price and lower output.
B) higher price and lower output.
C) higher price and higher output.
D) price and output that may be higher or lower.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The larger the number of firms and the less the degree of product differentiation, the greater will be the elasticity of a monopolistically competitive seller's demand curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monopolistic competition resembles pure competition because
A) both industries emphasize nonprice competition.
B) in both instances firms will operate at the minimum point on their long-run average total cost curves.
C) both industries entail the production of differentiated products.
D) barriers to entry are either weak or nonexistent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive producer is
A) less elastic than that of either a pure monopolist or a pure competitor.
B) less elastic than that of a pure monopolist, but more elastic than that of a pure competitor.
C) more elastic than that of a pure monopolist, but less elastic than that of a pure competitor.
D) more elastic than that of either a pure monopolist or a pure competitor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under monopolistic competition, entry to the industry is
A) completely free of barriers.
B) more difficult than under pure competition but not nearly as difficult as under pure monopoly.
C) more difficult than under pure monopoly.
D) blocked.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph depicts a monopolistically competitive firm. 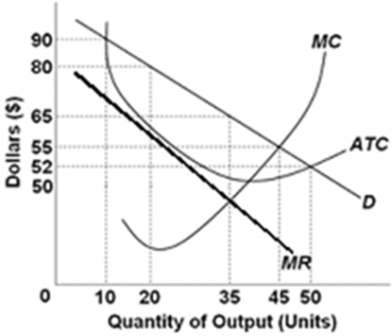 At the profit-maximizing level of short-run output, this monopolistically competitive firm will be making a profit of
At the profit-maximizing level of short-run output, this monopolistically competitive firm will be making a profit of
A) $275.
B) $350.
C) $500.
D) $525.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The more elastic a monopolistic competitor's long-run demand curve, the
A) greater its excess capacity.
B) higher its price relative to that of a pure competitor having the same cost curves.
C) lower its long-run economic profit.
D) lower its average total cost at its profit-maximizing level of output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The monopolistic competition model assumes that
A) allocative efficiency will be achieved.
B) productive efficiency will be achieved.
C) firms will engage in nonprice competition.
D) firms will realize economic profits in the long run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Concentration ratios measure the
A) geographic location of the largest corporations in each industry.
B) degree to which product price exceeds marginal cost in various industries.
C) percentage of total industry sales accounted for by the largest firms in the industry.
D) number of firms in an industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Herfindahl index for a pure monopolist is
A) 100.
B) 10,000.
C) 100,000.
D) 10.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monopolistic competition is characterized by a
A) few dominant firms and low entry barriers.
B) large number of firms and substantial entry barriers.
C) large number of firms and low entry barriers.
D) few dominant firms and substantial entry barriers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the four-firm concentration ratio in an oligopolistic industry is 100 percent and each firm has an equal percentage of sales, the Herfindahl index is
A) 10,000.
B) 2,500.
C) 3,750.
D) 1,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Excess capacity implies
A) productive inefficiency.
B) allocative inefficiency.
C) productive efficiency.
D) allocative efficiency.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium,
A) production takes place where ATC is minimized.
B) marginal revenue equals marginal cost and price equals average total cost.
C) normal profit is zero and price equals marginal cost.
D) economic profit is zero and price equals marginal cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 194
Related Exams