A) sensitivity of consumer purchases of a good to changes in the price of that good.
B) change in total utility obtained by consuming one more unit of a good.
C) change in total utility obtained by consuming another unit of a good divided by the change in the price of that good.
D) total utility associated with the consumption of a certain number of units of a good divided by the number of units consumed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the following two schedules, which show the amounts of additional satisfaction (marginal utility) that a consumer would get from successive quantities of products J and K. 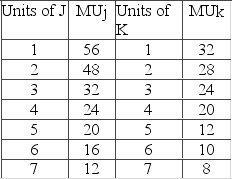 If the consumer has money income of $52 and the prices of J and K are $8 and $4 respectively, the consumer will maximize her utility by purchasing
If the consumer has money income of $52 and the prices of J and K are $8 and $4 respectively, the consumer will maximize her utility by purchasing
A) 2 units of J and 7 units of K.
B) 5 units of J and 5 units of K.
C) 4 units of J and 5 units of K.
D) 6 units of J and 3 units of K.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume MUc and MUd represent the marginal utility that a consumer gets from products C and D, the respective prices of which are Pc and Pd. The consumer will increase his total utility from a specific money outlay by spending more on C and less on D if initially
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To the average consumer, the marginal utility of a second copy of today's newspaper is
A) constant.
B) increasing.
C) close to zero.
D) close to one.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the diagram, where xy is the relevant budget line and I1, I2, and I3 are indifference curves. If the consumer is initially at point L, he or she should 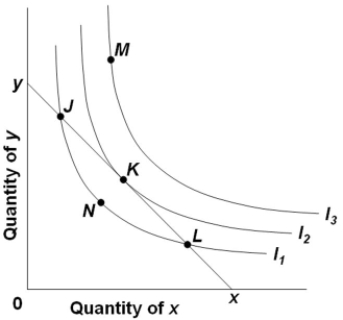
A) strive for point N by obtaining a larger money income.
B) purchase more of X and less of Y.
C) remain at that point to maximize utility.
D) purchase more of Y and less of X.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If two combinations of goods X and Y give a consumer equal satisfaction, then these two combinations must both be on the same
A) budget line.
B) indifference curve.
C) demand curve.
D) supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct?
A) Budget lines are linear and upsloping; indifference curves are downsloping and concave to the origin.
B) Budget lines are linear and downsloping; indifference curves are downsloping and concave to the origin.
C) Budget lines are linear and downsloping; indifference curves are downsloping and convex to the origin.
D) Budget lines are downsloping and convex to the origin; indifference curves are linear and downsloping.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Consider This) A topographical map shows successively higher equal-elevation lines, whereas an indifference map shows successively higher levels of total
A) utility.
B) revenue.
C) profit.
D) cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which situation is consistent with the law of diminishing marginal utility?
A) The more pizza Joe eats, the more he enjoys an additional slice.
B) The more pizza Joe eats, the less he enjoys an additional slice.
C) Joe's marginal utility from eating pizza becomes positive after eating three slices.
D) Joe's marginal utility from eating pizza reaches a maximum when total utility is zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How did Apple overcome consumers' diminishing marginal utility for iPads?
A) Apple lowered the price of iPads so that previous buyers would purchase another unit.
B) Apple introduced new features to entice previous buyers to purchase new models.
C) Apple ignored the problem and focused solely on attracting new buyers.
D) Apple was unable to overcome the problem and has faced steadily declining sales.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mr. Samuelson's current rates of purchase are such that the marginal utility of slacks is 18 and the marginal utility of ties for him is 5. If slacks and ties are priced at $12 and $2, respectively, it can be concluded that Mr. Samuelson
A) is spending too much on slacks and not enough on ties.
B) is spending too much on ties and not enough on slacks.
C) is spending his income in such a way as to maximize his satisfaction.
D) should buy six times as many ties as he does slacks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is possible that as a result of the budget line shifting outward, the consumer will buy less of a product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shows the total utility data for products X and Y. Assume that the prices of X and Y are $3 and $4, respectively, and that consumer income is $18. 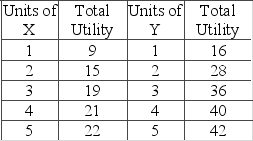 If the price of X decreases from $3 to $2, while the price of Y and the consumer's income stay the same, then the utility-maximizing combination is such that the quantity of X
If the price of X decreases from $3 to $2, while the price of Y and the consumer's income stay the same, then the utility-maximizing combination is such that the quantity of X
A) increases from 2 to 3.
B) decreases from 3 to 2.
C) stays the same at 2.
D) increases from 2 to 4.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shows the marginal-utility schedules for goods A and B for a hypothetical consumer. The price of good A is $1, and the price of good B is $2. The income of the consumer is $8.  If the price of B falls to $1, while the price of A and the consumer's income stay the same, what would be the utility-maximizing combination of goods A and B?
If the price of B falls to $1, while the price of A and the consumer's income stay the same, what would be the utility-maximizing combination of goods A and B?
A) 5 A and 3 B
B) 4 A and 4 B
C) 3 A and 5 B
D) 2 A and 6 B
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shows a consumer's utility schedule. 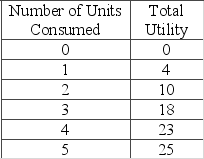 Marginal utility begins to diminish with the consumption of the
Marginal utility begins to diminish with the consumption of the
A) fifth unit.
B) fourth unit.
C) third unit.
D) second unit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the productivity of labor over time will
A) decrease the value of time.
B) increase the value of time.
C) decrease the demand for labor-saving devices.
D) decrease the demand for consumer goods and services.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in the real income of a consumer is one result from an increase in the price of a product that the consumer is buying.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The financing of health care through insurance has
A) decreased absolute total expenditures on health care.
B) resulted in consumers directly paying less than the full price of health care.
C) increased the marginal utility of health care services.
D) made no change in health care consumption.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Indifference analysis assumes that utility is numerically measurable.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where total utility is at a maximum, marginal utility is
A) negative.
B) positive and increasing.
C) zero.
D) positive but decreasing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 256
Related Exams