A) transferring a copy of an organism's entire genome to reproduce its traits.
B) manipulating original DNA sequences to "mutations" that may improve traits of interest.
C) All of these answer options are typical for cloning research methods.
D) selection of only one chromosome to transfer, bearing particular genes of interest.
E) selecting the sex of the offspring, extracting and transferring the sex chromosomes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When the genetic material of multiple organisms has been combined,it is called recombinant DNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A couple,both carriers of Cystic Fibrosis alleles,can prepare for a child being born with the disease,by testing with
A) preimplantation genetic diagnosis.
B) cloning and testing the unborn child.
C) gene therapy.
D) polymerase chain reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Analysis of data showed that humans and chimpanzees share ___ of common DNA sequences,and ___ of sequences (genes) coding for proteins.
A) 98%; 85%
B) three billion nucleotides; 25 thousand genes
C) 96%; 99%
D) 50%; 98%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many plants,fungi,and even animals can asexually reproduce new genetic copies of themselves because fragments survive.This is a natural version of
A) cloning.
B) meiosis.
C) mutation.
D) None of the answer choices are correct.
E) transgenic organisms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The genetic molecular material that has been spliced together from multiple organisms is
A) RNA transcriptase.
B) a zygote.
C) any specific protein produced from a gene.
D) recombinant DNA.
E) both (either) RNA transcriptase, and any specific protein produced from a gene.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A GMO is a transgenic organism.
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The first organism (organisms) to have been produced as transgenic organisms was (were)
A) eukaryotic yeasts.
B) agricultural plants.
C) viruses.
D) bacteria.
E) Dolly the cloned sheep.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis is one form of biotechnology associated with the fertility technology of
A) cloning.
B) adult stem cell research.
C) embryonic stem cell research.
D) the polymerase chain reaction.
E) in vitro fertilization.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After a cell has been removed from an embryo for preimplantation genetic diagnosis,the embryo
A) cannot develop into a fetus or baby.
B) will be used for gene therapy on parents or siblings.
C) will then be placed in a cloning chamber.
D) will continue to grow and develop.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Decorative flowers have been modified,from their wild type,to modern showy versions.Agricultural crops and livestock are selectively produced to have desirable nutrition and yield.Favorite dog and cat breeds exhibit desired traits of appearance and behavior.All of these are examples of
A) how strongly the traits and breeds of transgenic organisms have changed species already.
B) All of these answer options are correct.
C) many generations of traditional breeding techniques.
D) changes leading to new breeds, or entire new species can only be produced with transgenic organisms.
E) production of transgenic organisms by traditional breeding methods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The medical goal in applying gene therapy to diseased people is to find substitute genes from other organisms to cure the disease condition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Being cloned,Dolly exhibited differences from normally reproduced sheep,in that she
A) was able to reproduce asexually, without requirement of a male sperm.
B) gave birth to healthy lambs through normal sexual reproduction.
C) developed lung disease at a young age of six years.
D) developed both arthritis in her hind legs, and lung disease, dying at a young age.
E) developed arthritis in her hind legs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In medicine,agriculture,and conservation applications of biotechnology,the common genetic unit used is the
A) gene.
B) centromere.
C) nucleotide (nitrogen base) .
D) chromatid.
E) allele.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the correct comparison in the genetic characteristics between embryonic and adult stem cells.
A) Adult stem cells can produce any of the differentiated cells, while embryonic stem cells can't.
B) Embryonic stem cells are collected from the testes and ovaries, while adult stem cells are collected from other tissues.
C) Embryonic stem cells can produce any of the differentiated cells, while adult stem cells can't.
D) There is not real genetic difference between embryonic and adult stem cells, except how they were collected.
E) Embryonic stem cells are produced naturally in human development, while adult stem cells are from cloning.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The researcher (researchers) who first established the method for DNA sequencing was (were)
A) Ian Wilmut.
B) James Watson and Francis Crick.
C) Frederick Sanger.
D) Gregor Mendel.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Unlike plants,the production of transgenic animals commonly relies on viruses as cloning vectors.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the least practical option,if your personal genetic testing indicates the presence of a disease-causing allele.
A) You may decide as a potential parent, with your partner, to not have children.
B) You and your physician may seek treatment for the identified faulty protein(s) caused by the disease allele.
C) You will be certain of having the disease, but because it is genetic, you have limited medical options.
D) You and your physician may identify preventative measures before the disease advances.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:
The chromosomes of humans and chimpanzees look virtually identical in structure, size, and stained banding patterns. 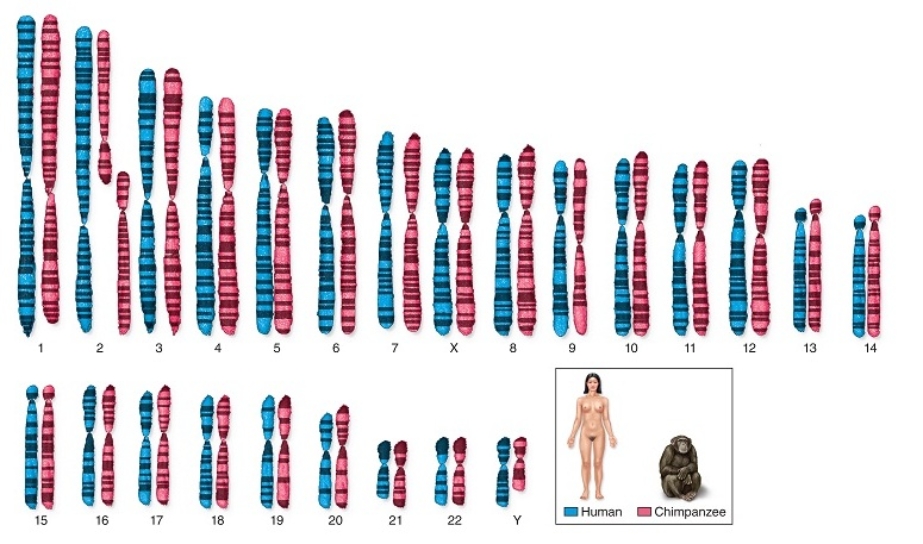 -The larges difference in chromosomes found between humans and chromosomes,at (human) chromosome 2,is hypothesized to be
-The larges difference in chromosomes found between humans and chromosomes,at (human) chromosome 2,is hypothesized to be
A) an evolutionary selection that merged two chromosomes in humans after evolving from a common ancestor with other primates.
B) the result of the specific family lineage of the chimpanzee, Clint, who provided the DNA and chromosome samples for study.
C) the only genetic difference that prevents humans and chimpanzees from closer resemblence, behaviors, and communication.
D) a widely divergent set of genes found in the human chromosome 2, that is not found in the shorter chimpanzee chromosomes.
E) None of the answer choices are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For DNA sequencing,the technological process called ___ separates DNA fragments that have already been isolated and cut into different lengths.
A) translation
B) electrophoresis
C) the polymerase chain reaction
D) binary fission
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 48
Related Exams