Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The protein derived from a particular gene is different when it is found in a neuron than in a muscle cell.This is most likely due to
A) alternative mRNA processing.
B) regulation of mRNA translation.
C) alteration of protein activity.
D) mRNA editing.
E) DNA excision.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the elongation cycle of translation,the A site on a ribosome functions in
A) receiving a new tRNA with the correct amino acid.
B) holding a polypeptide as amino acids are added.
C) attaching the small subunits of rRNA to the large subunit.
D) releasing the completed polypeptide.
E) processing the rRNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would be the most likely result on the regulation of the lac operon from a non-functional repressor protein?
A) transcription of the lactose metabolizing genes, even when lactose is absent
B) no transcription of the lactose metabolizing genes, even when lactose is present
C) binding of the repressor protein to the operator even when lactose is present
D) binding of the repressor protein to the regulatory gene in both the presence and absence of lactose
E) no transcription of the regulatory gene, even in the presence of lactose
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The stages of translation are
A) transcription, mRNA processing, and termination.
B) DNA replication, transcription, and termination.
C) initiation, transcription, elongation cycle, and termination.
D) initiation, elongation cycle, and termination.
E) initiation, transcription, mRNA processing, and termination.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following enzymes is needed to seal breaks in the sugar-phosphate backbone during replication?
A) DNA polymerase
B) RNA polymerase
C) RNA ligase
D) helicase
E) DNA ligase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events in gene expression control does not occur in the nucleus?
A) chromatin condensation
B) mRNA translation
C) DNA transcription
D) mRNA processing
E) transcription factor binding
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a DNA strand composed of the sequence AGT in the 5' to 3' direction,the free phosphate is on the ____ nucleotide and the free hydroxyl is on the ____ nucleotide.
A) T; A
B) A; G
C) A; A
D) G; T
E) A; T
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure: 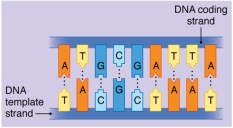 -The sequence of the mRNA that would result from transcribing the gene pictured would be
-The sequence of the mRNA that would result from transcribing the gene pictured would be
A) AUGCGAUUA.
B) AUUAGCGUA.
C) UACGCUAAU.
D) UAAUCGCAU.
E) ATGCGATTA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The two DNA strands must be separated before DNA replication or transcription can occur.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a DNA strand that is two nucleotides long,how many different sequences are possible?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
E) 64
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Chargaff's rules,___ always pairs with ____,and _____ always pairs with _____.
A) A; G; T; C
B) A; T; G; C
C) A; C; G; T
D) C; T; G; A
E) G; U; A; C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What chemical force must be overcome in order to separate the two DNA strands during replication?
A) hydrophobic interactions
B) intrastrand folding
C) ionic bonds
D) phosphodiester bonds
E) hydrogen bonds
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The three steps that are required for DNA replication are
A) unwinding, complementary base pairing, and joining.
B) base doubling, unwinding, and joining.
C) complementary base pairing, transcription, and translation.
D) unwinding, transcription, and translation.
E) unwinding, base doubling, and base pairing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Female mammals form Barr bodies because
A) compacting the chromatin of one of their X chromosomes allows them to inactivate it and produce the same amount of gene product as a male.
B) unpacking one of their X chromosomes allows them to produce more gene product than a male.
C) compacting the chromatin in one of their X chromosomes allows them to conserve histone proteins.
D) compacting the chromatin in one of their X chromosomes allows them to produce more gene product than a male from the other X chromosome.
E) unpacking one of their X chromosomes allows them to choose which allele they wish to express, which a male cannot do.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A defect in DNA ligase would most likely cause
A) normal replication, but gaps remain in the sugar-phosphate DNA backbone.
B) failure to remove introns from the primary mRNA.
C) incompletely processed primary mRNA that does not get translated properly.
D) translation to initiate normally, but fail to proceed to elongation.
E) DNA strands to separate normally, but fail to join nucleotides in the growing nucleotide chain.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA replication is called semiconservative because
A) one of the two resulting DNA molecules is new.
B) the two resulting DNA molecules each have one new DNA strand and one old strand from the original DNA molecule.
C) both of the resulting DNA molecules are composed of new strands of nucleotides.
D) no extra nucleotides are incorporated into the replicated DNA molecules.
E) the sequence of nucleotides in one strand is conserved, whereas the new DNA molecule consists of a unique sequence of nucleotides
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 57 of 57
Related Exams