A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2NH3 (g)  N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that the moles of
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that the moles of 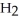 in the reaction container will increase with ________.
in the reaction container will increase with ________.
A) some removal of ![]() from the reaction vessel (V and T constant)
from the reaction vessel (V and T constant)
B) a decrease in the total pressure (T constant)
C) addition of some ![]() to the reaction vessel (V and T constant)
to the reaction vessel (V and T constant)
D) a decrease in the total volume of the reaction vessel (T constant)
E) an increase in total pressure by the addition of helium gas (V and T constant)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide?
5N2O4(g) ![Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the equilibrium between dinitrogen tetroxide and nitrogen dioxide? 5N<sub>2</sub>O4(g) 10NO<sub>2</sub> (g) A) [NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>10</sup>/[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>5</sup> B) [N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>10</sup>/[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup> C) [NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup>/[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>10</sup> D) [NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup>/[N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>5</sup> E) [N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>]<sup>5</sup>/[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>5</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1194/11ea7e7c_6154_e700_9a0a_71c6fe3fa864_TB1194_11.jpg) 10NO2 (g)
10NO2 (g)
A) [NO2]10/[N2O4]5
B) [N2O4]10/[NO2]5
C) [NO2]5/[N2O4]10
D) [NO2]5/[N2O4]5
E) [N2O4]5/[NO2]5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which reaction will shift to the left in response to a decrease in volume?
A) 2HI (g) ![]() H2 (g) + I2 (g)
H2 (g) + I2 (g)
B) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) ![]() 2 HCl (g)
2 HCl (g)
C) N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ![]() 2 NH3 (g)
2 NH3 (g)
D) 2 SO3 (g) ![]() 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
E) 4 Fe (s) + 3 O2 (g) ![]() 2 Fe2O3 (s)
2 Fe2O3 (s)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of Keq for the equilibrium N2 (g) + O2 (g)  2 NO (g)
Is 4.2 × 10-31 at 27 °C.What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
4 NO (g)
2 NO (g)
Is 4.2 × 10-31 at 27 °C.What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
4 NO (g)  2 N2 (g) + 2 O2 (g)
2 N2 (g) + 2 O2 (g)
A) 5.7 × 1060
B) 8.4 × 10-31
C) 4.2 × 1031
D) 8.4 × 1031
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Keq for the equilibrium below is 5.4 × 1013 at 480.0 °C. 2NO (g) + O2 (g)  2NO2 (g)
What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
4NO (g) + 2O2 (g)
2NO2 (g)
What is the value of Keq at this temperature for the following reaction?
4NO (g) + 2O2 (g)  4NO2 (g)
4NO2 (g)
A) 2.9 × 1027
B) 8.5 × 1054
C) 3.4 × 10-28
D) -1.1 × 1014
E) 5.4 × 1013
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: C (s) + H2O (g)  CO (g) + H2 (g)
Which of the following conditions will decrease the partial pressure of CO?
CO (g) + H2 (g)
Which of the following conditions will decrease the partial pressure of CO?
A) decreasing the volume of the reaction vessel
B) increasing the volume of the reaction vessel
C) decreasing the amount of carbon in the system
D) decreasing the pressure of the reaction vessel
E) adding a catalyst to the reaction system
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The equilibrium-constant expressed as 1/Keq is for a reaction written in the ________ direction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction below is exothermic: 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)  2SO3 (g)
Le Châtelier's Principle predicts that ________ will result in an increase in the number of moles of
2SO3 (g)
Le Châtelier's Principle predicts that ________ will result in an increase in the number of moles of 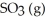 in the reaction container.
in the reaction container.
A) increasing the amount of SO2
B) decreasing the pressure
C) increasing the temperature
D) removing some oxygen
E) increasing the volume of the container
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equilibrium constant for the gas phase reaction 2SO3 (g)  2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Is Keq = 3.6 × 10-3 at 999 K.At equilibrium,________.
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Is Keq = 3.6 × 10-3 at 999 K.At equilibrium,________.
A) products predominate
B) reactants predominate
C) roughly equal amounts of products and reactants are present
D) only products are present
E) only reactants are present
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the endothermic reaction CaCO3 (s)  CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that ________ will result in an increase in the number of moles of
CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that ________ will result in an increase in the number of moles of 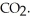
A) increasing the temperature
B) decreasing the temperature
C) increasing the pressure
D) removing some of the CaCO3(s)
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sealed 1.0 L flask is charged with 0.500 mol of I2 and 0.500 mol of Br2.An equilibrium reaction ensues: I2 (g) + Br2 (g)  2IBr (g)
When the container contents achieve equilibrium,the flask contains 0.84 mol of IBr.The value of
2IBr (g)
When the container contents achieve equilibrium,the flask contains 0.84 mol of IBr.The value of 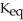 is ________.
is ________.
A) 11
B) 4.0
C) 110
D) 6.1
E) 2.8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dinitrogen tetroxide partially decomposes according to the following equilibrium: 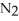
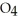 (g) →
(g) → 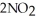 (g) A 1.000-L flask is charged with 9.20 × 10-3 mol of
(g) A 1.000-L flask is charged with 9.20 × 10-3 mol of 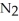
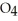 .At equilibrium,5.98 × 10-3 mol of
.At equilibrium,5.98 × 10-3 mol of 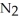
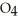 remains.
remains. 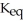 for this reaction is ________.
for this reaction is ________.
A) 0.183
B) 0.197
C) 0.212
D) 6.94 × ![]()
E) 2.96 × 10-5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following reaction at equilibrium at 450.0 °C: CaCO3 (s)  CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
If pCO2 = 0.0155 atm,Kc = ________.
CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
If pCO2 = 0.0155 atm,Kc = ________.
A) 155
B) 0.0821
C) 0.920
D) 2.61 × 10-4
E) 9.20
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of Keq for the following reaction is 0.16: A (g) + B (g)  C (g) + D (g)
The value of Keq at the same temperature for the reaction below is ________.
3C (g) + 3D (g)
C (g) + D (g)
The value of Keq at the same temperature for the reaction below is ________.
3C (g) + 3D (g)  3A (g) + 3B (g)
3A (g) + 3B (g)
A) 2.4 × 102
B) 2.1
C) 4.1 × 10-3
D) 5.3 × 10-2
E) 6.3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which reaction will shift to the right in response to a decrease in volume?
A) N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ![]() 2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g)
B) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) ![]() 2 HCl (g)
2 HCl (g)
C) 2 SO3 (g) ![]() 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
D) 2HI (g) ![]() H2 (g) + I2 (g)
H2 (g) + I2 (g)
E) 2 Fe2O3 (s) ![]() 4 Fe (s) + 3O2 (g)
4 Fe (s) + 3O2 (g)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following reaction at equilibrium,if Kc = 1.90 × 1019 at 25.0 °C,Kp = ________. H2 (g) + Br2 (g)  2 HBr (g)
2 HBr (g)
A) 5.26 × 10-20
B) 1.56 × 104
C) 6.44 × 105
D) 1.90 × 1019
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 97 of 97
Related Exams