A) strengthens the stimulative effect of an expansionary fiscal policy.
B) strengthens the stimulative effect of an expansionary monetary policy
C) weakens the stimulative effect of an expansionary monetary policy.
D) has no perceptible impact upon stabilization policies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Monetary policy is subject to less political pressure than fiscal policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that the Bank of Canada's policy is to keep the price level from either rising or falling.If aggregate supply increases in the economy,the Bank of Canada:
A) will have to increase interest rates to keep the price level from falling.
B) will have to reduce the money supply to keep the price level from rising.
C) will have to increase the money supply to keep the price level from falling.
D) can keep the price level stable without altering the money supply or interest rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correct?
A) The asset demand for money is downward sloping because the opportunity cost of holding money declines as the interest rate rises.
B) The asset demand for money is downward sloping because the opportunity cost of holding money increases as the interest rate rises.
C) The transactions demand for money is downward sloping because the opportunity cost of holding money varies inversely with the interest rate.
D) The asset demand for money is downward sloping because bond prices and the interest rate are directly related.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A restrictive monetary policy in Canada is most likely to:
A) depreciate the international value of the dollar and increase Canadian net exports.
B) depreciate the international value of the dollar and decrease Canadian net exports.
C) appreciate the international value of the dollar and increase Canadian net exports.
D) appreciate the international value of the dollar and decrease Canadian net exports.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the Bank of Canada sells $2 billion of government bonds to the public,which pays for them by drawing cheques.As a result,chartered bank reserves will:
A) increase by $10 billion.
B) remain unchanged.
C) decrease by $2 billion.
D) increase by $2 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A disequilibrium in the market for money is mainly corrected via a change in:
A) bond prices.
B) the price level.
C) saving levels.
D) the money supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If in the market for money the quantity of money demanded exceeds the money supply,we would expect the interest rate to:
A) fall,causing households and businesses to hold less money.
B) rise,causing households and businesses to hold less money.
C) rise,causing households and businesses to hold more money.
D) fall,causing households and businesses to hold more money.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the Bank of Canada creates excess reserves in the banking system by buying government bonds,but banks do not make more loans because economic conditions are bad.This situation is a problem of:
A) cyclical asymmetry.
B) a restrictive monetary policy.
C) the net export effect.
D) a decrease in the velocity of money.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the money GDP is $600 billion and,on the average,each dollar is spent three times per year,then the amount of money demanded for transactions purposes:
A) will be $1800 billion.
B) will be $600 billion.
C) will be $200 billion.
D) cannot be determined from the information given.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following is a simplified consolidated balance sheet for the chartered banking system and the Bank of Canada. Assume a desired reserve ratio of 5 percent for the chartered banks. All figures are in billions of dollars.
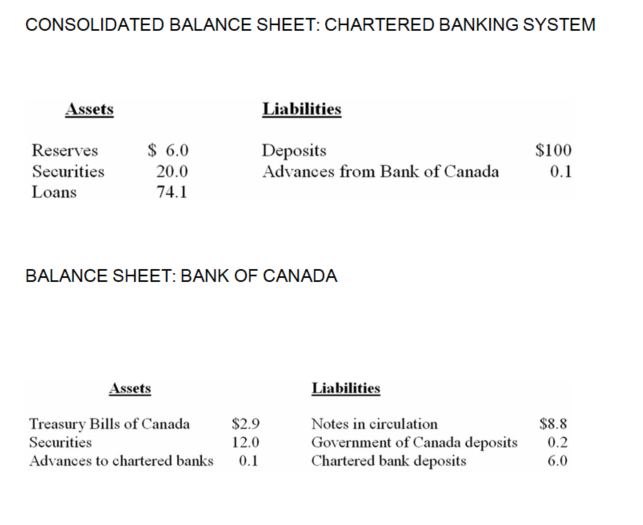 -Refer to the above information,suppose the Bank of Canada sells $2 in securities directly to the chartered banks.As a result of this transaction,the supply of money:
-Refer to the above information,suppose the Bank of Canada sells $2 in securities directly to the chartered banks.As a result of this transaction,the supply of money:
A) will directly increase by $2 and the money-creating potential of the chartered banking system will increase by $38.
B) will directly decrease by $2 and the money-creating potential of the chartered banking system will decrease by $40.
C) is not directly affected,but the money-creating potential of the chartered banking system will decrease by $40.
D) will decrease by $2,but the money-creating potential of the chartered banking system will not be affected.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The reason for the Bank of Canada to have a range for its inflation targeting is that some of the components of the CPI,fluctuate a lot.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following are simplified consolidated balance sheets for the chartered banking system and the Bank of Canada.Do not cumulate your answers;that is,do return to the data given in the original balance sheets in answering each question.Assume a desired reserve ratio of 5 percent for the chartered banks.All figures are in billions of dollars.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET: CHARTERED BANKING SYSTEM
 BALANCE SHEET: BANK OF CANADA
BALANCE SHEET: BANK OF CANADA
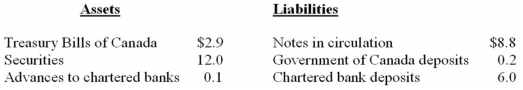 -Refer to the above information.The chartered banks have excess reserves of:
-Refer to the above information.The chartered banks have excess reserves of:
A) $1
B) $6
C) $20
D) $0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Interest rates and bond prices vary directly.
B) Interest rates and bond prices vary inversely.
C) Interest rates and bond prices are unrelated.
D) Interest rates and bond prices vary directly during inflations and inversely during recessions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A headline reads: "Bank of Canada raises the overnight rate by half a point." This indicates that:
A) fiscal policy is being offset by monetary policy.
B) monetary policy is being offset by fiscal policy.
C) there has been a tightening of monetary policy.
D) there has been an easing of monetary policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The monetary authorities can influence the money supply by:
A) changing bank reserves through the sale of government securities.
B) changing the amounts of excess reserves by persuading banks to alter their desired reserve ratio.
C) changing the bank reserves through the purchase of government securities.
D) doing all of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An important routine function of the Bank of Canada is:
A) to help new chartered banks sell capital stock.
B) to supply the economy with paper currency.
C) to advise chartered banks as to the most profitable ways of reinvesting profits.
D) to help chartered banks develop correspondent relationships with foreign banks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the consolidated balance sheet of the Bank of Canada,loans to chartered banks are:
A) a liability of the Bank of Canada and chartered banks.
B) an asset of the Bank of Canada and chartered banks.
C) a liability of the Bank of Canada and an asset for chartered banks.
D) an asset of the Bank of Canada and a liability for chartered banks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 238 of 238
Related Exams