A) Demand is elastic when Q > a/2b.
B) Demand is inelastic when Q > a/b.
C) Demand is unit elastic when P = a/2b.
D) Demand is elastic when Q < a/2b.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist faces a demand curve and that the monopolist has a constant marginal cost of 75. The monopolist's profit-maximizing price is
A) 25
B) 50
C) 75
D) 100
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions:
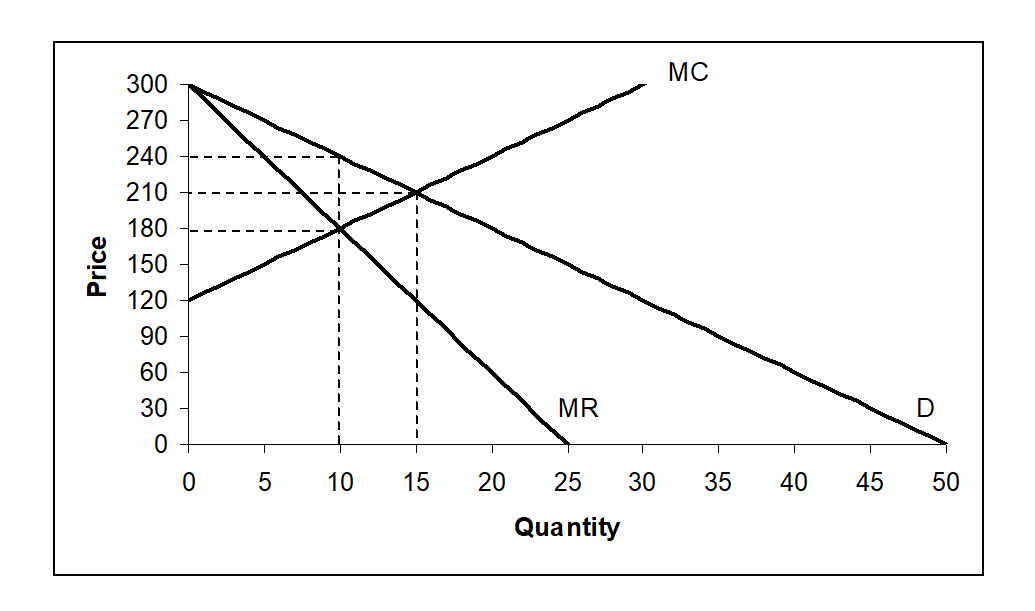 -The total economic benefit under perfect competition would be
-The total economic benefit under perfect competition would be
A) 2,700
B) 1,350
C) 675
D) 500
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Monopoly profits are generally zero.
B) Monopoly profits are maximized when total revenue is maximized.
C) The condition, MC = MR, is the optimizing condition for monopolists and firms in perfectly competitive markets.
D) Usually the demand and marginal revenue curves for a monopoly are the same.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best explains why there is no meaningful supply curve for a monopolist?
A) The monopolist is the only supplier.
B) Price is exogenous to the monopolist.
C) The monopolist is already maximizing profits; thus, it doesn't need a supply curve.
D) Price is endogenous. That is, the monopolist determines both quantity and price. Hence, there is no longer a unique association between price and quantity supplied.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following examples comes the closest to describing a monopsony market?
A) The market for beryllium.
B) The market for Microsoft Windows.
C) The market for breakfast cereal.
D) The market for United States military uniforms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Lerner Index for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry would be
A) less than zero.
B) zero.
C) between zero and one.
D) one.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist owns two plants in which to produce a product which has inverse demand P = (770/3) - 3Q. The monopolist has marginal cost curves of MC1 = 20+3Q1 and MC2 = 10+6Q2 in the two plants, respectively. Which of the following represents the optimal outputs in the two plants, Q1 and Q2 and the market price?
A) Q1 = 170/9; Q2 = 100/9; P = 500/3.
B) Q1 = 100/9; Q2 = 170/9; P = 500/3.
C) Q1 = 500/3; Q2 = 170/9; P = 100/9.
D) Q1 = 500/3; Q2 = 100/9; P = 170/9.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a monopolist's demand curve becomes more inelastic,
A) the profit-maximizing price goes up.
B) the profit-maximizing price goes down.
C) the optimal mark-up of price over marginal cost goes down.
D) average revenue falls.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order to calculate the Lerner Index for a particular firm, you need to know _______ and ______ for that firm.
A) marginal cost; marginal revenue
B) marginal cost; price
C) price; quantity
D) price; demand
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One argument for allowing monopolies to exist is
A) it would be inefficient to break up natural monopolies into smaller units.
B) monopolies lead to net economic benefits as a rule.
C) the free market acts as a more effective regulator than the government.
D) they allow for greater standardization of products and improved quality control.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopolist
A) selling price is greater than average revenue.
B) selling price is equal to average revenue.
C) selling price is less than average revenue.
D) selling price may be above or below average revenue; it depends on the price buyers are willing to pay.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a monopolist's marginal cost shifts upward,
A) total revenue will remain unchanged.
B) total revenue will increase.
C) total revenue will fall.
D) total revenue may rise or fall depending on the slope of the demand curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The term product differentiation refers to:
A) A situation in which two or more products possess technical differences, which may or may not be perceived by consumers.
B) A situation in which two or more products possess attributes that, in the minds of consumers, set the products apart from one another and make them less than perfect substitutes.
C) A situation in which two or more firms produce products for a given market.
D) A situation in which two or more consumers purchase differing amounts of a product in a market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a monopolist faces a demand curve Q = aP-b and that the monopolist has a constant marginal cost of C. The monopolist's profit-maximizing price is
A)
B)
C)
D) P = C(-1/b)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist faces inverse demand and has marginal cost . What price should this monopolist charge to maximize profit?
A) 10
B) 50
C) 210
D) 240
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following diagram to answer the following questions:
 -The total economic benefit under monopoly would be
-The total economic benefit under monopoly would be
A) 300
B) 600
C) 900
D) 1,200
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the false statement.
A) A monopolist and a perfectly competitive firm both maximize profits.
B) A monopolist and a perfectly competitive firm both produce an output level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
C) A monopolist and a perfectly competitive firm both produce where price equals marginal cost.
D) A monopolist and a perfectly competitive firm both charge a price based on the demand curve facing the firm and the costs borne by the firm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist will produce where
A) demand is elastic.
B) demand is perfectly elastic.
C) demand is inelastic.
D) demand is perfectly inelastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To compute the optimal monopoly price with a linear demand curve, the monopolist
A) should set MC = MR, which would determine the optimal quantity and price would equal MC and MR as well.
B) should set MC = MR, which would determine the optimal quantity and price would be found by inserting the optimal quantity into the monopolist's demand curve.
C) should set MC = MR, which would determine the optimal quantity and price would be found by doubling the marginal cost.
D) should set output where total revenue would be the greatest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 65
Related Exams