A) the quantity of one good exchanged for a unit of another good.
B) the world price of a good determined by the world supply and demand for the good.
C) the quantity of a good demanded by U.S. consumers at a market-clearing price.
D) the price of a good in a country after the imposition of a tariff.
E) the maximum amount of credit that a country can borrow for a particular line of credit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following graph shows U.S. demand for and domestic supply of a good. Suppose the world price of the good is $1.00 per unit and a specific tariff of $0.50 per unit is imposed on each unit of imported good. In such a case, the loss of consumer surplus as a result of a tariff of $0.50 per unit is represented by the area _____.
Figure 19.2
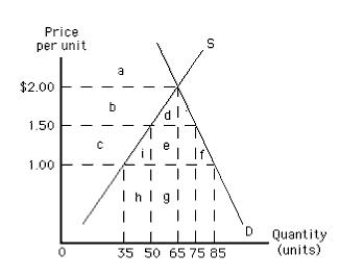
A) a
B) b + d
C) c + i + e + f
D) c
E) d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of autarky?
A) Each country's consumption possibilities are the same as its production possibilities.
B) Equilibrium is attained with the maximum gains from specialization and trade.
C) There is no legal limit on the amount of a commodity that can be imported.
D) Countries export products they can produce more cheaply in return for products that are unavailable domestically or are cheaper elsewhere.
E) World price is determined by the world supply and demand for a product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following was a motive of the United States to negotiate a free trade agreement with Mexico?
A) To help foster the study of the Spanish language as a means to trade with all Spanish-speaking countries
B) To increase immigration into the United States
C) To gain increased access to Mexican consumers
D) To attract more Mexican investment
E) To achieve political union with Mexico
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An effective import quota:
A) lowers the price of imports.
B) lowers the price of domestic goods competing with imports.
C) increases the variety of goods available to the consumer.
D) increases federal revenues.
E) lowers the quantity of the imported good.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following table shows the demand, supply, and price of tulips in the Netherlands. If the world price of tulips is $1 and there are no trade restrictions, the Netherlands will:
Table 19.2
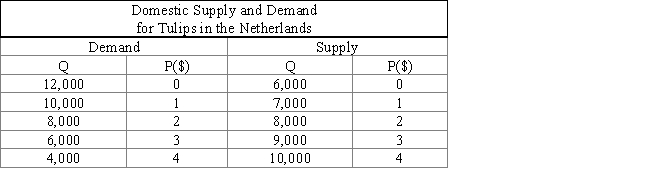
A) produce 7,000, consume 10,000, and export 3,000 tulips.
B) produce 10,000 and consume 10,000 tulips.
C) produce 9,000, consume 6,000, and export 6,000 tulips.
D) import all of the tulips that it consumes.
E) consume all of the tulips that it produces.
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a two-country, two-commodity framework, when one country has an absolute advantage in the production of both commodities, _____.
A) autarky is always preferred to trade
B) differences in the opportunity cost of production between the two countries ensure that specialization and trade result in mutual gains
C) the country with the lowest opportunity cost of production is the least competitive in international markets
D) the countries gain from mutual trade as long as tastes differ across countries
E) the countries gain from specialization and exchange as long as they are the same size
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between the effects of an import quota and a tariff is that:
A) only the tariff results in a higher domestic price.
B) only the quota decreases the amount of goods imported.
C) the decrease in producer surplus is smaller with the quota.
D) under a quota, part of the decrease in consumer surplus is redistributed to foreign producers; under a tariff, it is redistributed to the domestic government.
E) under a tariff, part of the decrease in consumer surplus is redistributed to foreign producers; under a quota, it is redistributed to the domestic government.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following reasons best explains why the United States is a net importer of crude oil and metals and a net exporter of farm crops?
A) Differences in resource endowments
B) Economies of scale
C) Differences in tastes
D) Import quota
E) Import tariffs
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the United States has an absolute advantage in producing computer components, it should export them worldwide.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
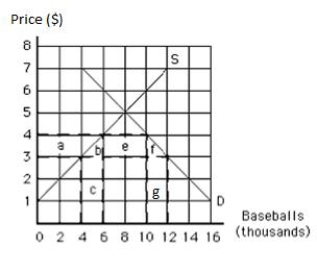
The following graph shows the supply of and demand for baseballs in the United States. If the world price of a baseball is $3, then the quantity of baseballs demanded is _____.
Figure 19.3
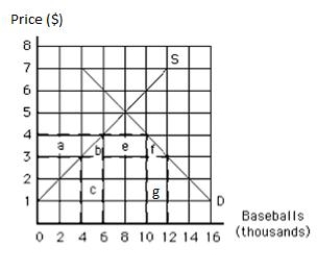
A) 4,000
B) 6,000
C) 8,000
D) 10,000
E) 12,000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Dumping refers to selling a commodity abroad at a price that is below its cost of production or below the price charged in the domestic market.
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The World Trade Organization (WTO) :
A) became, in 1995, the institutionalized and more comprehensive successor to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) .
B) was established in 1947 by 23 member countries to reduce trade restrictions.
C) was established in 1980 to oppose and counteract the policies of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) .
D) meets in different countries every few years to analyze each country's trade policies and restrictions.
E) was based on an international treaty that expired in 1990.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The international treaty established to negotiate lower trade restrictions is known as the:
A) World Bank Act.
B) General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) .
C) International Association for Free Trade (IAFT) .
D) Countries United for Free Trade (CUFT) .
E) International Development Fund.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following graph shows the supply of and demand for baseballs in the United States. If the world price is $3 per baseball, then _____ baseballs are imported.
Figure 19.3
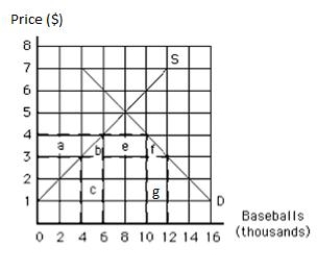
A) 4,000
B) 6,000
C) 8,000
D) 10,000
E) 12,000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an argument in favor of restricting trade?
A) Preserving national security
B) Preventing dumping
C) Increasing consumer surplus
D) Protecting infant industries
E) Protecting declining industries
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not true of dumping?
A) In the country where products are dumped, consumer surplus grows as a result of the dumping.
B) Dumping involves the selling of a product by foreign producers at a price lower than that in their own countries.
C) Critics of dumping recommend applying a tariff as a correct antidumping measure.
D) A major difficulty with dumping by firms in other countries is that it drives up prices for the domestic consumer.
E) Predatory dumping is often aimed at driving domestic producers out of business.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was established in:
A) 1870 to protect U.S. industries and decrease world trade.
B) 1921 to manage legal and accounting requirements for U.S. tariffs and quotas.
C) 1947 by 23 countries to reduce trade restrictions.
D) 1973 to increase trade restrictions, after OPEC significantly raised oil prices.
E) 1990 to develop a free trade zone across 50 states.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following graph shows the supply of and demand for baseballs in the United States. If the world price is $3 per baseball and a tariff of $1 per baseball is imposed, then the number of baseballs imported is _____.
Figure 19.3
A) 4,000
B) 6,000
C) 8,000
D) 10,000
E) 12,000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a manufacturer sells goods abroad for a lesser price than they sell for at home, it implies that _____.
A) an embargo has been established
B) a quota has been imposed
C) the manufacturer is engaged in dumping
D) there has been an improvement in the terms of trade
E) tariffs have been reduced
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 150
Related Exams