A) 5, 000 decks
B) 10, 000 decks
C) 15, 000 decks
D) 20, 000 decks
E) 25, 000 decks
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Provided a firm does not use an extreme amount of debt, financial leverage typically affects both EPS and EBIT, while operating leverage only affects EBIT.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Barette Consulting currently has no debt in its capital structure, has $500 million of total assets, and its basic earning power is 15%.The CFO is contemplating a recapitalization where it will issue debt at a cost of 10% and use the proceeds to buy back shares of the company's common stock, paying book value.If the company proceeds with the recapitalization, its operating income, total assets, and tax rate will remain unchanged.Which of the following is most likely to occur as a result of the recapitalization?
A) The ROA would remain unchanged.
B) The basic earning power ratio would decline.
C) The basic earning power ratio would increase.
D) The ROE would increase.
E) The ROA would increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT associated with (or does not contribute to) business risk? Recall that business risk is affected by a firm's operations.
A) Sales price variability.
B) The extent to which operating costs are fixed.
C) The extent to which interest rates on the firm's debt fluctuate.
D) Input price variability.
E) Demand variability.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) The capital structure that maximizes the stock price is generally the capital structure that also maximizes earnings per share.
B) All else equal, an increase in the corporate tax rate would tend to encourage a company to increase its debt ratio.
C) Since debt financing raises the firm's financial risk, increasing a company's debt ratio will always increase its WACC.
D) Since debt is cheaper than equity, increasing a company's debt ratio will always reduce its WACC.
E) When a company increases its debt ratio, the costs of equity and debt both increase.Therefore, the WACC must also increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A venture capital investment group received a proposal from Wireless Solutions to produce a new smart phone.The variable cost per unit is estimated at $250, the sales price would be set at twice the VC/unit, fixed costs are estimated at $750, 000, and the investors will put up the funds if the project is likely to have an operating income of $500, 000 or more.What sales volume would be required in order to meet this profit goal?
A) 4, 513
B) 4, 750
C) 5, 000
D) 5, 250
E) 5, 513
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cartwright Communications is considering making a change to its capital structure to reduce its cost of capital and increase firm value.Right now, Cartwright has a capital structure that consists of 20% debt and 80% equity, based on market values.(Its D/S ratio is 0.25.) The risk-free rate is 6% and the market risk premium, rM - rRF, is 5%.Currently the company's cost of equity, which is based on the CAPM, is 12% and its tax rate is 40%.What would be Cartwright's estimated cost of equity if it were to change its capital structure to 50% debt and 50% equity?
A) 13.00%
B) 13.64%
C) 14.35%
D) 14.72%
E) 15.60%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Exhibit 15.3.Now assume that BB is considering changing from its original capital structure to a new capital structure with 45% debt and 55% equity.This results in a weighted average cost of capital equal to 10.4% and a new value of operations of $576, 923.Assume BB raises $259, 615 in new debt and purchases T-bills to hold until it makes the stock repurchase.BB then sells the T-bills and uses the proceeds to repurchase stock.How many shares remain after the repurchase, and what is the stock price per share immediately after the repurchase?
A) 11, 001; $28.85
B) 12, 711; $35.62
C) 13, 901; $42.57
D) 15, 220; $54.31
E) 17, 105; $89.67
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Exhibit 15.1.PP is considering changing its capital structure to one with 30% debt and 70% equity, based on market values.The debt would have an interest rate of 8%.The new funds would be used to repurchase stock.It is estimated that the increase in risk resulting from the added leverage would cause the required rate of return on equity to rise to 12%.If this plan were carried out, what would be PP's new value of operations?
A) $484, 359
B) $487, 805
C) $521, 173
D) $560, 748
E) $584, 653
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things held constant, which of the following events is most likely to encourage a firm to increase the amount of debt in its capital structure?
A) The costs that would be incurred in the event of bankruptcy increase.
B) Management believes that the firm's stock has become overvalued.
C) Its degree of operating leverage increases.
D) The corporate tax rate increases.
E) Its sales become less stable over time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The world-famous discounter, Fernwood Booksellers, specializes in selling paperbacks for $7 each.The variable cost per book is $5.At current annual sales of 200, 000 books, the publisher is just breaking even.It is estimated that if the authors' royalties are reduced, the variable cost per book will drop by $1.Assume authors' royalties are reduced and sales remain constant; how much more money can the publisher put into advertising (a fixed cost) and still break even?
A) $600, 000
B) $466, 667
C) $333, 333
D) $200, 000
E) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bailey and Sons has a levered beta of 1.10, its capital structure consists of 40% debt and 60% equity, and its tax rate is 40%.What would Bailey's beta be if it used no debt, i.e., what is its unlevered beta?
A) 0.64
B) 0.67
C) 0.71
D) 0.75
E) 0.79
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Exhibit 15.3.BB is considering moving to a capital structure that is comprised of 20% debt and 80% equity, based on market values.The debt would have an interest rate of 7%.The new funds would be used to repurchase stock.It is estimated that the increase in risk resulting from the additional leverage would cause the required rate of return on equity to rise to 14%.If this plan were carried out, what would BB's new value of operations be?
A) $498, 339
B) $512, 188
C) $525, 237
D) $540, 239
E) $590, 718
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
As the text indicates, a firm's financial risk has identifiable market risk and diversifiable risk components.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
LeCompte Learning Solutions is considering making a change to its capital structure in hopes of increasing its value.The company's capital structure consists of debt and common stock.In order to estimate the cost of debt, the company has produced the following table:
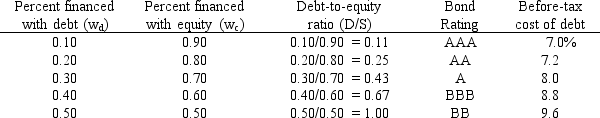 The company uses the CAPM to estimate its cost of common equity, rs.The risk-free rate is 5% and the market risk premium is 6%.LeCompte estimates that if it had no debt its beta would be 1.0.(Its "unlevered beta, " bU, equals 1.0.) The company's tax rate, T, is 40%.
On the basis of this information, what is LeCompte's optimal capital structure, and what is the firm's cost of capital at this optimal capital structure?
The company uses the CAPM to estimate its cost of common equity, rs.The risk-free rate is 5% and the market risk premium is 6%.LeCompte estimates that if it had no debt its beta would be 1.0.(Its "unlevered beta, " bU, equals 1.0.) The company's tax rate, T, is 40%.
On the basis of this information, what is LeCompte's optimal capital structure, and what is the firm's cost of capital at this optimal capital structure?
A) wc = 0.9; wd = 0.1; WACC = 14.96%
B) wc = 0.8; wd = 0.2; WACC = 10.96%
C) wc = 0.7; wd = 0.3; WACC = 7.83%
D) wc = 0.6; wd = 0.4; WACC = 10.15%
E) wc = 0.5; wd = 0.5; WACC = 10.18%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Laramie Trucking's CEO is considering a change to the company's capital structure, which currently consists of 25% debt and 75% equity.The CFO believes the firm should use more debt, but the CEO is reluctant to increase the debt ratio.The risk-free rate, rRF, is 5.0%, the market risk premium, RPM, is 6.0%, and the firm's tax rate is 40%.Currently, the cost of equity, rs, is 11.5% as determined by the CAPM.What would be the estimated cost of equity if the firm used 60% debt? (Hint: You must first find the current beta and then the unlevered beta to solve the problem.)
A) 10.95%
B) 11.91%
C) 12.94%
D) 14.07%
E) 15.29%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An all-equity firm with 200, 000 shares outstanding, Antwerther Inc., has $2, 000, 000 of EBIT, which is expected to remain constant in the future.The company pays out all of its earnings, so earnings per share (EPS) equal dividends per shares (DPS) .Its tax rate is 40%. The company is considering issuing $5, 000, 000 of 10.0% bonds and using the proceeds to repurchase stock.The risk-free rate is 6.5%, the market risk premium is 5.0%, and the beta is currently 0.90, but the CFO believes beta would rise to 1.10 if the recapitalization occurs. Assuming that the shares can be repurchased at the price that existed prior to the recapitalization, what would the price be following the recapitalization?
A) $65.77
B) $69.23
C) $72.69
D) $76.33
E) $80.14
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Since debt financing is cheaper than equity financing, raising a company's debt ratio will always reduce its WACC.
B) Increasing a company's debt ratio will typically reduce the marginal cost of both debt and equity financing.However, this action still may raise the company's WACC.
C) Increasing a company's debt ratio will typically increase the marginal cost of both debt and equity financing.However, this action still may lower the company's WACC.
D) Since a firm's beta coefficient it not affected by its use of financial leverage, leverage does not affect the cost of equity.
E) Since debt financing raises the firm's financial risk, increasing a company's debt ratio will always increase its WACC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Exhibit 15.4.Now assume that AJC is considering changing from its original capital structure to a new capital structure with 50% debt and 50% equity.If it makes this change, its resulting market value would be $820, 000.What would be its new stock price per share?
A) $58
B) $59
C) $60
D) $61
E) $62
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Exhibit 15.1.Assume that PP is considering changing from its original capital structure to a new capital structure with 35% debt and 65% equity.This results in a weighted average cost of capital equal to 9.4% and a new value of operations of $510, 638.Assume PP raises $178, 723 in new debt and purchases T-bills to hold until it makes the stock repurchase.PP then sells the T-bills and uses the proceeds to repurchase stock.How many shares remain after the repurchase, and what is the stock price per share immediately after the repurchase?
A) 7, 500; $71.49
B) 7, 000; $59.57
C) 6, 500; $51.06
D) 6, 649; $53.33
E) 6, 959; $58.78
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 72
Related Exams