A) hold more money and the quantity of aggregate goods and services demanded increases.
B) hold more money and the quantity of aggregate goods and services demanded decreases.
C) hold less money and the quantity of aggregate goods and services demanded increases.
D) hold less money and the quantity of aggregate goods and services demanded decreases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following lists includes only changes that shift aggregate demand to the right?
A) repeal of an investment tax credit, an increase in the money supply
B) repeal of an investment tax credit, a decrease in the money supply
C) passing of an investment tax credit, an increase in the money supply
D) passing of an investment tax credit, a decrease in the money supply
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most commonly used to monitor short-run changes in economic activity?
A) the inflation rate.
B) real GDP.
C) interest rates.
D) value of the U.S. dollar in the foreign exchange market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a determinant of the long-run level of real GDP?
A) the price level.
B) the amount of capital used by firms.
C) available stock of human capital.
D) available technology
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same, as the price level rises, the real value of a dollar
A) rises, and interest rates rise.
B) rises, and interest rates fall.
C) falls, and interest rates rise.
D) falls, and interest rates fall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Figure 33-13. 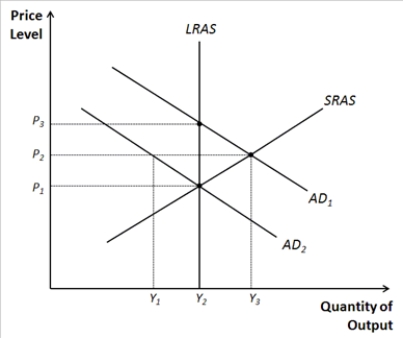 Refer to Figure 33-13. Identify the price and output levels consistent with long-run equilibrium.
Refer to Figure 33-13. Identify the price and output levels consistent with long-run equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a stock market crash makes people feel poorer. This decrease in wealth would induce people to
A) decrease consumption, which shifts aggregate supply left.
B) decrease consumption, which shifts aggregate demand left.
C) increase consumption, which shifts aggregate supply right.
D) increase consumption, which shifts aggregate demand right.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following both shift aggregate demand left?
A) a decrease in taxes and at a given price level consumers feel more wealthy
B) a decrease in taxes and at a given price level consumers feel less wealthy
C) an increase in taxes and at a given price level consumers feel more wealthy
D) an increase in taxes and at a given price level consumers feel less wealthy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same, the aggregate quantity of goods demanded in the U.S. increases if
A) real wealth rises.
B) the interest rate rises.
C) the dollar appreciates.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price level falls, the real value of a dollar
A) rises, so people will want to buy more. This response helps explain the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
B) rises, so people will want to buy more. This response shifts aggregate demand to the right.
C) falls, so people will want to buy less. This response helps explain the slope of the aggregate demand curve.
D) falls, so people will want to buy less. This response shifts aggregate demand to the left.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most economists believe that classical theory describes the world
A) in the short run.
B) in the long run.
C) in both the short run and the long run.
D) in neither the short run nor the long run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same, if the price level is lower than expected, then some firms believe that the relative price of what they produce has
A) decreased, so they increase production.
B) decreased, so they decrease production.
C) increased, so they increase production.
D) increased, so they decrease production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate-demand curve
A) has a slope that is explained in the same way as the slope of the demand curve for a particular product.
B) is vertical in the long run.
C) shows an inverse relation between the price level and the quantity of all goods and services demanded.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The variables on the vertical and horizontal axes of the aggregate demand and supply graph are
A) the price level and real output.
B) real output and employment.
C) employment and the inflation rate.
D) the value of money and the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same, which of the following is correct?
A) A decrease in the price level causes the dollar to appreciate. Aggregate demand shifts right.
B) A decrease in the price level causes the dollar to depreciate. Aggregate demand shifts right.
C) If speculators lose confidence in the American economy, the dollar appreciates. Aggregate demand shifts right.
D) If speculators lose confidence in the American economy, the dollar depreciates. Aggregate demand shifts right.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same, as the price level falls, which of the following increases?
A) lending and investment spending
B) lending, but not investment spending
C) investment spending, but not lending
D) neither investment spending nor lending
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Real and nominal variables are highly intertwined, and changes in the money supply change real GDP. Most economists would agree that this statement accurately describes
A) both the short run and the long run.
B) the short run, but not the long run.
C) the long run, but not the short run.
D) neither the long run nor the short run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The saying "Money is a veil." means that
A) while nominal variables are the first thing we may observe about an economy, what's important are the real variables and the forces that determine them.
B) money is the principal medium of exchange in most economies.
C) the primary determinant of short-run economic fluctuations is not real variables, but rather changes in the money supply.
D) in the long run money is of no importance to the determination of either real or nominal variables.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same, when the price level rises, interest rates
A) rise, which means consumers will want to spend more on homebuilding.
B) rise, which means consumers will want to spend less on homebuilding.
C) fall, which means consumers will want to spend more on homebuilding.
D) fall, which means consumers will want to spend less on homebuilding.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following alone can explain the change in the price level and output during World War II?
A) aggregate demand shifted right
B) aggregate demand shifted left
C) aggregate supply shifted right
D) aggregate supply shifted left
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 381 - 400 of 563
Related Exams