A) a clear area in the center of the cell
B) chromosomes clustered at the poles
C) individual chromatids beginning to separate from one another
D) chromosomes clustered tightly at the center
E) breaking down of the nuclear envelope
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a cleavage furrow?
A) a ring of vesicles forming a cell plate
B) the separation of divided prokaryotes
C) a groove in the plasma membrane between daughter nuclei
D) the metaphase plate where chromosomes attach to the spindle
E) the space that is created between two chromatids during anaphase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Density-dependent inhibition is explained by which of the following?
A) As cells become more numerous, they begin to squeeze against each other, restricting their size and ability to produce control factors.
B) As cells become more numerous, the cell surface proteins of one cell contact the adjoining cells and they stop dividing.
C) As cells become more numerous, the protein kinases they produce begin to compete with each other, such that the proteins produced by one cell essentially cancel those produced by its neighbor.
D) As cells become more numerous, more and more of them enter the S phase of the cell cycle.
E) As cells become more numerous, the level of waste products increases, eventually slowing down metabolism.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do neurons and some other specialized cells divide infrequently?
A) They no longer have active nuclei.
B) They no longer carry receptors for signal molecules.
C) They have been shunted into G0.
D) They can no longer bind Cdk to cyclin.
E) They show a drop in MPF concentration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Proteins that are involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, and that show fluctuations in concentration during the cell cycle, are called
A) ATPases.
B) kinetochores.
C) kinases.
D) estrogen receptors.
E) cyclins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Movement of the chromosomes during anaphase would be most affected by a drug that prevents
A) nuclear envelope breakdown.
B) cell wall formation.
C) elongation of microtubules.
D) shortening of microtubules.
E) formation of a cleavage furrow.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a protein synthesized at specific times during the cell cycle that associates with a kinase to form a catalytically active complex?
A) PDGF
B) MPF
C) protein kinase
D) cyclin
E) Cdk
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have a series of cells, all of which were derived from tumors, and you first need to find out which ones are malignant. What could you do?
A) See which ones are not overproliferating.
B) Find out which ones have a higher rate of apoptosis.
C) Karyotype samples to look for unusual size and number of chromosomes.
D) Measure metastasis.
E) Time their cell cycles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes are composed of DNA
A) and RNA.
B) only.
C) and proteins.
D) and phospholipids.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a chemotherapeutic drug to be useful for treating cancer cells, which of the following is most desirable?
A) It is safe enough to limit all apoptosis.
B) It does not alter metabolically active cells.
C) It only attacks cells that are density dependent.
D) It interferes with cells entering G0.
E) It interferes with rapidly dividing cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the data in Table 9.1 to answer the following questions.
The data were obtained from a study of the length of time spent in each phase of the cell cycle by cells of three eukaryotic organisms designated beta, delta, and gamma.
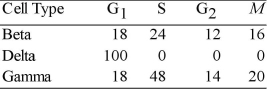 Table 9.1
Minutes Spent in Cell Cycle Phases
-The best conclusion concerning delta is that the cells
Table 9.1
Minutes Spent in Cell Cycle Phases
-The best conclusion concerning delta is that the cells
A) contain no DNA.
B) contain no RNA.
C) contain only one chromosome that is very short.
D) are actually in the G0 phase.
E) divide in the G1 phase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following triggers the cell's passage past the G2 checkpoint into mitosis?
A) PDGF
B) MPF
C) protein kinase
D) cyclin
E) Cdk
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A plant-derived protein known as colchicine can be used to poison cells by blocking the formation of the spindle. Which of the following would result if colchicine is added to a sample of cells in G2?
A) The cells would immediately die.
B) The cells would be unable to begin M and stay in G2.
C) The chromosomes would coil and shorten but have no spindle to which to attach.
D) The chromosomes would segregate but in a disorderly pattern.
E) Each resultant daughter cell would also be unable to form a spindle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During which phase of mitosis do the chromatids become chromosomes?
A) telophase
B) anaphase
C) prophase
D) metaphase
E) cytokinesis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following most accurately describes a cyclin?
A) It is present in similar concentrations throughout the cell cycle.
B) It is activated to phosphorylate by complexing with a Cdk.
C) It decreases in concentration when MPF activity increases.
D) It activates a Cdk molecule when it is in sufficient concentration.
E) It activates a Cdk when its concentration is decreased.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on Figure 9.3.
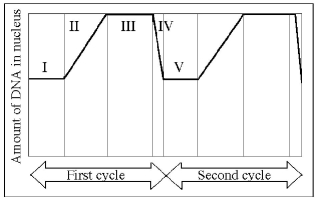 Figure 9.3
-Which number represents DNA synthesis?
Figure 9.3
-Which number represents DNA synthesis?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Humans produce skin cells by mitosis and gametes by meiosis. The nuclei of skin cells produced by mitosis will have
A) half as much DNA as the nuclei of gametes produced by meiosis.
B) the same amount of DNA as the nuclei of gametes produced by meiosis.
C) twice as much DNA as the nuclei of gametes produced by meiosis.
D) four times as much DNA as the nuclei of gametes produced by meiosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
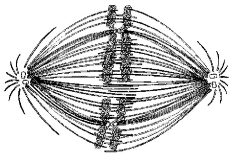 Figure 9.2
-If the cell whose nuclear material is shown in Figure 9.2 continues toward completion of mitosis, which of the following events would occur next?
Figure 9.2
-If the cell whose nuclear material is shown in Figure 9.2 continues toward completion of mitosis, which of the following events would occur next?
A) cell membrane synthesis
B) spindle fiber formation
C) nuclear envelope breakdown
D) formation of telophase nuclei
E) synthesis of chromatids
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below.
The unlettered circle at the top of Figure 9.1 shows a diploid nucleus with four chromosomes that have not yet replicated. There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes, one long and the other short. One haploid set is black, and the other is gray. The circles labeled A-E show various combinations of these chromosomes. 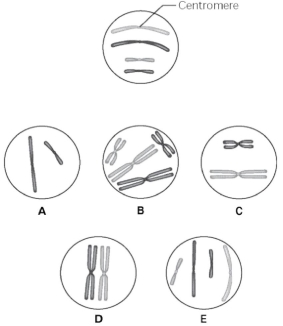 Figure 9.1
-What is the correct chromosomal condition for one daughter nucleus at telophase of mitosis?
Figure 9.1
-What is the correct chromosomal condition for one daughter nucleus at telophase of mitosis?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the data in Table 9.1 to answer the following questions.
The data were obtained from a study of the length of time spent in each phase of the cell cycle by cells of three eukaryotic organisms designated beta, delta, and gamma.
 Table 9.1
Minutes Spent in Cell Cycle Phases
-Of the following, the best conclusion concerning the difference between the S phases for beta and gamma is that
Table 9.1
Minutes Spent in Cell Cycle Phases
-Of the following, the best conclusion concerning the difference between the S phases for beta and gamma is that
A) gamma contains more DNA than beta.
B) beta and gamma contain the same amount of DNA.
C) beta cells reproduce asexually.
D) gamma contains 48 times more DNA and RNA than beta.
E) beta is a plant cell and gamma is an animal cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 63
Related Exams