A) all types of asexual reproduction.
B) all types of sexual reproduction.
C) fission.
D) fragmentation.
E) parthenogenesis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Like many other fishes, bluehead wrasses utilize harem mating as they reproduce sexually. However, unlike most fishes,
A) they also reproduce by fission.
B) they function without any signaling by steroid hormones.
C) they undergo a prolonged menopause during low tide.
D) their offspring can be either haploid or diploid.
E) large females morph into reproductively competent males.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During human gestation, rudiments of all organs develop
A) in the first trimester.
B) in the second trimester.
C) in the third trimester.
D) during the blastocyst stage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prior to ovulation, the primary steroid hormone secreted by the growing follicle is
A) luteinizing hormone (LH) .
B) follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) .
C) inhibin.
D) gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) .
E) estradiol.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
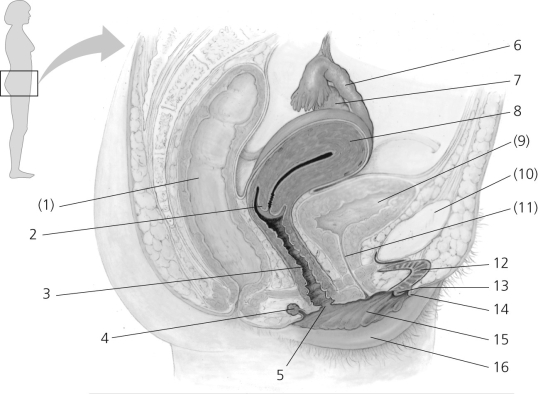 Figure 36.1
Some nonreproductive structures are labeled in parentheses for orientation purposes.
-In Figure 36.1, which number corresponds to the oviduct?
Figure 36.1
Some nonreproductive structures are labeled in parentheses for orientation purposes.
-In Figure 36.1, which number corresponds to the oviduct?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 12
E) 13
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
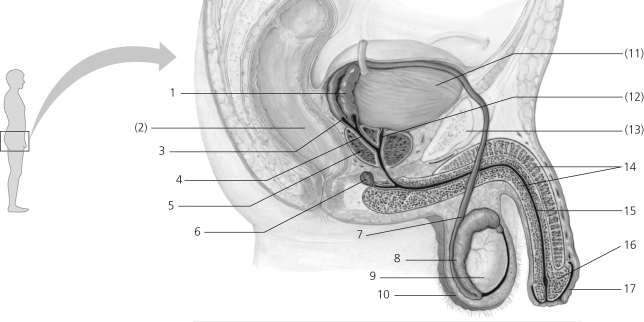 Figure 36.2
Some nonreproductive structures are labeled in parentheses for orientation purposes.
-In the figure, which numbers correspond to the vas deferens?
Figure 36.2
Some nonreproductive structures are labeled in parentheses for orientation purposes.
-In the figure, which numbers correspond to the vas deferens?
A) 1, 4
B) 2, 6
C) 8, 13
D) 3, 7
E) 5, 12
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An advantage of asexual reproduction is that it
A) allows the species to endure long periods of unstable environmental conditions.
B) enhances genetic variability in the species.
C) enables the species to rapidly colonize habitats that are favorable to that species.
D) produces offspring that respond effectively to new pathogens.
E) allows a species to easily rid itself of harmful mutations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An oocyte released from a human ovary enters the oviduct as a result of
A) the beating action of the flagellum on the oocyte.
B) the force of the follicular ejection directing the oocyte into the oviduct.
C) the wavelike beating of cilia lining the oviduct.
D) movement of the oocyte through the pulsating uterus into the oviduct.
E) peristaltic contraction of ovarian muscles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The use of birth control pills (oral contraceptives)
A) reduces the incidence of ovulation.
B) prevents fertilization by keeping the sperm and egg physically separated by a mechanical barrier.
C) prevents implantation of an embryo.
D) prevents sperm from exiting the male urethra.
E) prevents oocytes from entering the uterus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the choice that correctly associates the organ with its embryonic sources.
A) pituitary gland-mesoderm and endoderm
B) thyroid gland-mesoderm and ectoderm
C) adrenal gland (adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex) -ectoderm and mesoderm
D) skin-endoderm and mesoderm
E) jaws-mesoderm and endoderm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sexual reproduction patterns include
A) fragmentation.
B) budding.
C) hermaphroditism.
D) parthenogenesis.
E) fission.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Springtails are a type of arthropod. Male springtails drop tiny beads of semen attached to stalks. Females that are ready to reproduce search out these drops and take them into their genital opening. This is an example of
A) external fertilization without copulation.
B) external fertilization with copulation.
C) internal fertilization without copulation.
D) internal fertilization with copulation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A male's "primary" sex characteristics include
A) deepening of the voice at puberty.
B) embryonic differentiation of the seminal vesicles.
C) growth of skeletal muscle.
D) elongation of the skeleton prior to puberty.
E) onset of growth of facial hair at puberty.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone from the anterior pituitary gland is reduced by
A) inhibin.
B) luteinizing hormone.
C) oxytocin.
D) prolactin.
E) vasopressin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fertilization normally
A) reinstates diploidy.
B) follows gastrulation.
C) merges two diploid cells into one haploid cell.
D) precedes ovulation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A reproductive difference between sea urchins and humans is that
A) the sea urchin egg completes meiosis prior to fertilization, but meiosis in humans is completed after fertilization.
B) sea urchin eggs are produced by meiosis, but human eggs are produced by mitosis.
C) sea urchin eggs and sperm are of equal size, but human eggs are much bigger than human sperm.
D) sea urchins, but not humans, have a need to block polyspermy because only in sea urchins can there be more than one source of sperm to fertilize the eggs.
E) sea urchin zygotes get their mitochondria from the sperm, but human zygotes get their mitochondria from the egg.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As an embryo develops, new cells are produced as the result of
A) differentiation.
B) preformation.
C) cell division.
D) morphogenesis.
E) epigenesis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If gastrulation was blocked by an environmental toxin, then
A) cleavage would not occur in the zygote.
B) embryonic germ layers would not form.
C) fertilization would be blocked.
D) the blastula would not be formed.
E) internal fertilization could not occur.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the evolutionary "enigmas," or unsolved puzzles, of sexual reproduction is that
A) sexual reproduction allows for more rapid population growth than does asexual reproduction.
B) only half of the offspring from sexually reproducing females are also females.
C) asexual reproduction produces offspring of greater genetic variety.
D) sexual reproduction is completed more rapidly than asexual reproduction.
E) asexual reproduction is better suited to environments with extremely varying conditions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The junction of the upper vagina and the uterus is called the
A) fallopian tube.
B) clitoris.
C) oviduct.
D) labia majora.
E) cervix.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 118
Related Exams