A) New microtubules with more effective binding capabilities to kinetochores will be synthesised to compensate for the defect.
B) Excessive cell divisions will occur resulting in cancerous tumours and an increase in the chromosome numbers known as polyploidy.
C) The defect will be bypassed in order to ensure normal chromosome distribution in the new cells.
D) The resulting cells will not receive the correct number of chromosomes in the gametes, a condition known as aneuploidy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy is a human disorder that causes gradual deterioration of the muscles. Only boys are affected, and they are always born to phenotypically normal parents. Due to the severity of the disease, the boys die in their teens. Is this disorder likely to be caused by a dominant or recessive allele? Is the inheritance of this trait sex-linked or autosomal?
A) dominant, sex-linked
B) recessive, autosomal
C) recessive, sex-linked
D) incomplete dominant, sex-linked
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In Drosophila melanogaster, vestigial wings are determined by a recessive allele of a gene that is linked to a gene with a recessive allele that determines black body colour. Thomas H Morgan (1907) crossed black-bodied, normal-winged females and grey-bodied, vestigial-winged males. The F1 were all grey bodied, normal winged. The F1 females were crossed to homozygous recessive males to produce testcross progeny. Morgan calculated the map distance to be 17 map units. Which of the following information is correct about the testcross progeny?
A) black-bodied, normal-winged flies = 17% of the total
B) black-bodied, normal-winged flies plus grey-bodied, vestigial-winged flies = 17% of the total
C) grey-bodied, normal-winged flies plus black-bodied, vestigial-winged flies = 17% of the total
D) black-bodied, vestigial-winged flies = 17% of the total
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mitochondrial DNA is primarily involved in coding for proteins needed for protein complexes of the electron transport chain and ATP synthase. Therefore, mutations in mitochondrial genes would most affect which of the following processes?
A) DNA synthesis in cells of the immune system.
B) The movement of oxygen into erythrocytes.
C) Generation of ATP in muscle cells.
D) The storage of urine in the urinary bladder.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is generally true of aneuploidies in newborns?
A) A monosomy is more frequent than a trisomy.
B) Monosomy X is the only viable monosomy known to occur in humans.
C) Human aneuploidy usually conveys an adaptive advantage in humans.
D) An aneuploidy resulting in the deletion of a chromosome segment is less serious than a duplication.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding gene linkage is correct?
A) The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them.
B) The observed frequency of recombination of two genes that are far apart from each other has a maximum value of 100%.
C) All of the traits that Mendel studied-seed colour, pod shape, flower colour, and others-are due to genes linked on the same chromosome.
D) Linked genes are found on different chromosomes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A plant-like organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine. A geneticist performed a testcross with an organism that had been found to be heterozygous for the three recessive traits, and she was able to identify progeny of the following phenotypic distribution (+ = wild type) : - Which of the progeny phenotypes will require recombination between genes A and B?
A) 1, 2, 5, and 6
B) 1, 3, 6, and 7
C) 2, 4, 5, and 8
D) 2, 3, 5, and 7
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PD) is inherited as an X-linked recessive allele in humans. A woman whose father suffered from G6PD marries a normal man. What proportion of their sons is expected to be G6PD?
A) 100%
B) 1/4
C) 1/2
D) zero
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
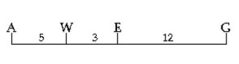 Between which two genes would you expect the highest frequency of recombination?
Between which two genes would you expect the highest frequency of recombination?
A) A and W
B) E and G
C) A and E
D) A and G
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A recessive allele on the X chromosome is responsible for red-green colour blindness in humans. A woman with normal vision whose father is colour blind marries a colour-blind male. What is the probability that this couple's first son will be colour blind?
A) 1/4
B) 1/2
C) 2/3
D) 3/4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following correctly describes a Philadelphia chromosome?
A) A human chromosome 22 that has had a specific translocation.
B) A human chromosome 9 that is found only in one type of cancer.
C) An animal chromosome found primarily in the mid-Atlantic area of the United States.
D) A chromosome found only in mitochondria.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following individuals will inherit an X-linked allele from a man who carries it?
A) all of his daughters
B) half of his daughters
C) all of his sons
D) all of his children
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In cats, black fur colour is determined by an X-linked allele; the other allele at this locus determines orange colour. The heterozygote is tortoiseshell. What kinds of offspring would you expect from the cross of a black female and an orange male?
A) tortoiseshell females; tortoiseshell males
B) black females; orange males
C) tortoiseshell females; black males
D) orange females; black males
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
German scientist, Carl Correns, found that the inheritance of variegated colour on the leaves of certain plants was determined only by the maternal parent. What phenomenon explains this pattern of inheritance?
A) ribosome structure
B) inheritance of plastid genes
C) genomic imprinting
D) sex linkage
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A man who is a dwarf with achondroplasia and normal vision marries a colour-blind woman of normal height. The man's father was six feet tall, and both the woman's parents were of average height. Dwarfism caused by achondroplasia is autosomal dominant, and red-green colour blindness is X-linked recessive. What proportion of their sons would be colour blind and of normal height?
A) none
B) half
C) one out of four
D) all
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A man who is a dwarf with achondroplasia and normal vision marries a colour-blind woman of normal height. The man's father was six feet tall, and both the woman's parents were of average height. Dwarfism caused by achondroplasia is autosomal dominant, and red-green colour blindness is X-linked recessive. How many of their daughters might be expected to be colour-blind with achondroplasia?
A) none
B) half
C) one out of four
D) three out of four
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A phenotypically normal prospective couple seeks genetic counselling because the man knows that he has a translocation of a portion of his chromosome 4, which has been exchanged with a portion of his chromosome 12. Although his translocation is balanced, he and his wife want to know the probability that his sperm will be abnormal. What is your prognosis regarding his sperm?
A) One-quarter will carry the two normal chromosomes, 4 and 12, one-quarter will have only the two translocation chromosomes and no normal chromosomes 4 and 12, and half will have one normal and one translocated chromosome.
B) All will carry the same translocation as the father.
C) None will carry the translocation.
D) Half will be normal, and the rest will have the father's translocation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sex determination in mammals is due to the SRY gene found on the Y chromosome. Which of the following situations could allow a person with an XX karyotype to develop a male phenotype?
A) The loss of the SRY gene from an autosome.
B) Translocation of SRY to an X chromosome.
C) The presence of an extra autosomal chromosome.
D) The presence of one normal and one shortened (deleted) X.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 58 of 58
Related Exams