A) combat inflation.
B) combat recessions.
C) encourage private saving.
D) make businesses more efficient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Discretionary fiscal policy
A) may not have desired effects on real GDP because of the time lags.
B) may not have desired effects on real GDP because it leads to increases in aggregate demand.
C) may not have desired effects on real GDP because it leads to decreases in aggregate demand.
D) would have a larger effect on real GDP if the multiplier was smaller.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of an automatic stabilizer is
A) the progressive tax system.
B) the decision of the President to cut taxes in a recession.
C) the Congressional decision to increase unemployment benefits in a recession.
D) the raising of taxes on cigarettes to discourage smoking to stabilize health-care costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The time that elapses between the implementation of a policy and its intended result is referred to as
A) the action time lag.
B) the recognition time lag.
C) the effect time lag.
D) the data lag.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whenever government spending is a substitute for private spending
A) interest rates will rise.
B) the Ricardian equivalence theorem holds.
C) the effects of expansionary fiscal policy are dampened.
D) there is a direct multiplier effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Automatic stabilizers have the effect of
A) increasing aggregate demand during a recessionary gap.
B) increasing aggregate demand during an inflationary gap.
C) increasing long-run aggregate supply during a recessionary gap.
D) increasing long-run aggregate supply during an inflationary gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An advantage of automatic stabilizers over discretionary fiscal policy is that
A) automatic stabilizers are not subject to the same time lags as discretionary fiscal policy.
B) automatic stabilizers can be easily fine-tuned to move the economy to full employment.
C) only the President is involved in implementing automatic stabilizers,instead of both the President and Congress.
D) the Ricardian equivalence theorem applies more readily to automatic stabilizers than to discretionary fiscal policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fiscal policy time lags tend to be
A) constant,always thirteen months long.
B) variable,between one and three years.
C) variable,between one and three weeks.
D) variable,between one and three months.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
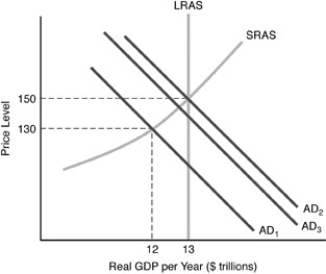 -Refer to the above figure.Suppose that the economy starts at
-Refer to the above figure.Suppose that the economy starts at 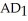 .If the government reduces taxes,then the economy goes to
.If the government reduces taxes,then the economy goes to 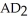 ,but then falls back to
,but then falls back to 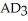 .This is an example of
.This is an example of
A) partial crowding-out effect.
B) Ricardian equivalence.
C) laissez-faire.
D) complete crowding-out effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to supply-side economics,changes in marginal tax rates will have which of the following effects?
A) change the incentive to work
B) change the incentive to save
C) change the incentive to invest
D) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is NOT an automatic stabilizer?
A) the income tax system
B) the system of national defense procurement
C) the system of welfare payments
D) unemployment compensation programs
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One characteristic of built-in or automatic stabilizers is that
A) they require no new legislative action by Congress to have an effect.
B) they automatically produce surpluses during recessions and deficits during inflation.
C) they have no effect on the distribution of income.
D) they reduce the size of the public debt during times of recession.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Discretionary fiscal policy is so named because it
A) is undertaken at the order of the nation's central bank.
B) occurs automatically as the nation's level of GDP changes.
C) involves specific changes in taxes and government spending undertaken by Congress and the president.
D) involves secret advice given by the Council of Economic Advisers to the president.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government increases aggregate demand when the economy is at both short-run and long-run equilibrium,the full long-run effect of this fiscal policy will be to
A) increase real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) .
B) increase the price level.
C) increase either the real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) or the price level,depending on the length of the time lag.
D) decrease both real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Discretionary fiscal policy is best described as
A) a deliberate attempt to cause the economy to move to full employment and price stability more quickly than it might otherwise.
B) a deliberate attempt to improve the functioning of free markets.
C) an automatic change in income transfer payments to keep the economy at full employment.
D) the design of a tax system that automatically stabilizes economic activity over time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The theory that government borrowing may function like an increase in taxes,that is,reducing current consumption and business expenditures,is known as
A) the marginal propensity to consume.
B) the Ricardian equivalence theorem.
C) planned tax policy.
D) Congressional Tax policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the government cuts taxes or increases government spending
A) the long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
B) the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
C) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
D) the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During normal times,discretionary fiscal policy
A) is more effective in influencing real GDP than at times of a recession.
B) is probably not very effective in influencing real GDP due to time lags.
C) is more effective in influencing real GDP than automatic stabilizers.
D) works well because there are no lag problems in influencing real GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Provisions that cause changes in government spending and taxes that do not require action of the President or Congress are called
A) discretionary fiscal policy.
B) discretionary stabilizers.
C) automatic stabilizers.
D) private stabilization effects.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During which time will fiscal policy be the most effective?
A) Normal times
B) Times of war
C) In the middle of expansions
D) Times of stagflation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 181 - 200 of 273
Related Exams