A) Oxygen and aluminum have no affinity for one another.
B) The oxidation of aluminum is not a favored process, as seen by the standard reduction potential for Al3+.
C) Aluminum forms a protective oxide coating.
D) At least two of these are correct.
E) Aluminum is not protected from corrosion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An excess of finely divided iron is stirred up with a solution that contains Cu2+ ion, and the system is allowed to come to equilibrium. The solid materials are then filtered off, and electrodes of solid copper and solid iron are inserted into the remaining solution. What potential develops between these two electrodes at 25°C?
A) 0
B) 0.592 V
C) 0.296 V
D) -0.78 V
E) Not enough information is given.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gold is produced electrochemically from an aqueous solution of Au(CN) 2- containing an excess of CN-. Gold metal and oxygen gas are produced at the electrodes. How many moles of O2 will be produced during the production of 1.00 mol of gold?
A) 4.00 mol
B) 3.56 mol
C) 0.50 mol
D) 1.00 mol
E) 0.25 mol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nickel is electroplated from a NiSO4 solution. A constant current of 5.72 amp is applied by an external power supply. How long will it take to deposit 2.08 × 102 g of Ni? (The atomic mass of Ni is 58.69 g/mol.)
A) 16.6 h
B) 33.2 h
C) 1.51 h
D) 19.9 min
E) 49.8 h
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A strip of copper is placed in a 1 M solution of copper nitrate, and a strip of silver is placed in a 1 M solution of silver nitrate. The two metal strips are connected to a voltmeter by wires, and a salt bridge connects the solutions. The following standard reduction potentials apply:  When the voltmeter is removed and the two electrodes are connected by a wire, which of the following does not take place?
When the voltmeter is removed and the two electrodes are connected by a wire, which of the following does not take place?
A) Negative ions pass through the salt bridge from the silver half-cell to the copper half-cell.
B) The silver electrode increases in mass as the cell operates.
C) Electrons flow in the external circuit from the copper electrode to the silver electrode.
D) Some positive copper ions pass through the salt bridge from the copper half-cell to the silver half-cell.
E) There is a net general movement of silver ions through the salt bridge to the copper half-cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is/are true of the electrolysis of brine? 1) Chlorine is produced at the anode of the cell during the electrolysis of brine. 2) Under normal circumstances, sodium is produced at the cathode of the cell during the electrolysis of brine. 3) Hydrogen is produced at the cathode of the cell during the electrolysis of brine.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1 and 3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the following equation
ΔG = ΔG° + RT 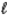 nK
nK
A) K = 1
B) ΔG° = 0
C) ΔG = ΔG°
D) ΔG = 0
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider an electrochemical cell with a copper electrode immersed in 1.0 M Cu2+ and a silver electrode immersed in 1.0 M Ag+.  -Which of the electrodes is the anode?
-Which of the electrodes is the anode?
A) the silver electrode
B) the copper electrode
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ammonium metavanadate reacts with sulfur dioxide in acidic solution as follows (hydrogen ions and H2O omitted) : XVO3- + ySO2 → xVO2+ + ySO42- The ratio x : y is
A) 1 : 3
B) 1 : 2
C) 2 : 1
D) 3 : 1
E) 1 : 1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following data to calculate the Ksp value at 25°C for PbSO4(s) . 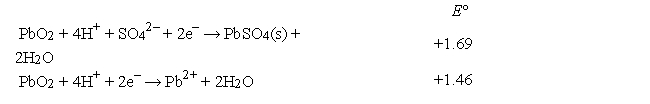
A) 3.89 × 10-105
B) 2.57 × 10105
C) 1.7 × 10-8
D) 5.9 × 107
E) None of these is within 5% of the correct answer.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a common car battery, six identical cells each carry out the following reaction: Pb + PbO2 + 2HSO4- + 2H+ → 2PbSO4 + 2H2O Suppose that to start a car on a cold morning, 138 amperes is drawn for 12.0 seconds from such a cell. How many grams of Pb are consumed? (The atomic mass of Pb is 207.19 g/mol.)
A) 0.562 g
B) 7.11 g
C) 1.78 g
D) 0.01235 g
E) 3.56 g
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction Cr(s) + NO3-(aq) → Cr3+(aq) + NO(g) takes place in acidic solution. -What is the coefficient of H2O(l) in the balanced equation?
A) 3
B) 5
C) 4
D) 2
E) 1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the galvanic cell shown below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment) .  The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows:  What is the value of E for this cell at 25°C?
What is the value of E for this cell at 25°C?
A) 1.88 V
B) 2.12 V
C) 1.76 V
D) 2.21 V
E) 0.59 V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a constant current of 5.2 amperes is passed through a cell containing Cr3+ for 2.1 hour, how many grams of Cr will plate out onto the cathode? (The atomic mass of Cr is 51.996 g/mol.)
A) 0.12 g
B) 1.1 g
C) 64 g
D) 21 g
E) 7.1 g
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What quantity of charge is required to reduce 32.6 g of CrCl3 to chromium metal? (1 faraday = 96,485 coulombs)
A) 3.97 × 104 C
B) 7.95 × 104 C
C) 5.96 × 104 C
D) 1.81 × 105 C
E) 1.99 × 104 C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is/are true of metal plating? 1) Metals that readily corrode can be protected by the application of a thin coating of a metal that resists corrosion. 2) An object can be plated with metal by making it the cathode in a tank containing ions of the plating metal. 3) An object can be plated with metal by making it the anode in a tank containing ions of the plating metal.
A) 2 only
B) 3 only
C) 1 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1 and 3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solution of MnO42- is electrolytically reduced to Mn3+. A current of 8.46 amp is passed through the solution for 15.0 minutes. What is the number of moles of Mn3+ produced in this process? (1 faraday = 96,485 coulombs)
A) 0.000438 mol
B) 0.0197 mol
C) 0.0789 mol
D) 0.0395 mol
E) 0.0263 mol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider an electrochemical cell with a copper electrode immersed in 1.0 M Cu2+ and a silver electrode immersed in 1.0 M Ag+. ![Consider an electrochemical cell with a copper electrode immersed in 1.0 M Cu<sup>2+</sup> and a silver electrode immersed in 1.0 M Ag<sup>+</sup>. If [Cu<sup>2+</sup>]<sub>0</sub> is 0.0038 M and [Ag<sup>+</sup>]<sub>0</sub> is 0.27 M, calculate E. A) 0.41 V B) 0.50 V C) 0.42 V D) 0.51 V E) 0.59 V](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6422/11eaaf91_9e0d_bb7a_892c_eb25b03f24ae_TB6422_00.jpg)
If [Cu2+]0 is 0.0038 M and [Ag+]0 is 0.27 M, calculate E.
If [Cu2+]0 is 0.0038 M and [Ag+]0 is 0.27 M, calculate E.
A) 0.41 V
B) 0.50 V
C) 0.42 V
D) 0.51 V
E) 0.59 V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the galvanic cell below (the contents of each half-cell are written beneath each compartment) . 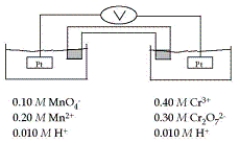 The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
The standard reduction potentials are as follows: 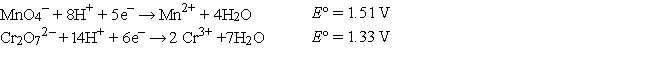 -What is the cell potential at 25°C as read on the digital voltmeter?
-What is the cell potential at 25°C as read on the digital voltmeter?
A) 0.18 V
B) 2.58 V
C) 0.59 V
D) 0.10 V
E) 0.26 V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction below occurs in basic solution. In the balanced equation, what is the sum of the coefficients? Zn + NO3- → Zn(OH) 42- + NH3
A) 27
B) 19
C) 23
D) 12
E) 15
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 90
Related Exams