A) N-methyl-2-ethyl-5-methyloctanamide
B) 6,N-dimethylnonane-3-carboxamide
C) 5,N-dimethyl-2-ethyloctanamide
D) 2-ethyl-5,N-dimethyloctanamide
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most characteristic IR stretch of butanenitrile occurs at approximately what wavenumber?
A) 3500 cm-1
B) 3100 cm-1
C) 2600 cm-1
D) 2200 cm-1
E) 1750 cm-1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Provide the major organic product in the reaction shown below. 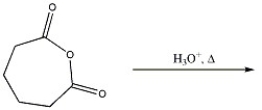
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Provide the IUPAC name for HCONHCH2CH2CH3.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Provide the major organic product of the following reaction. 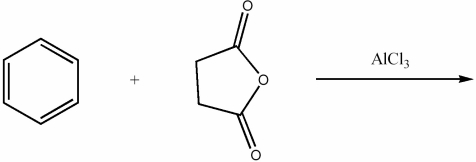
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Provide the name of the compound shown below. 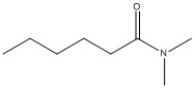
Correct Answer

verified
N, N-dimet...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Which sequence correctly lists the following structures in order of increasing rate of hydrolysis to a carboxylic acid under basic conditions? 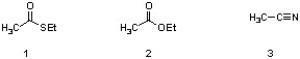
A) 1 < 2 < 3
B) 2 < 3 < 1
C) 3 < 1 < 2
D) 3 < 2 < 1
E) 2 < 1 < 3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Provide the major organic product of the following reaction. 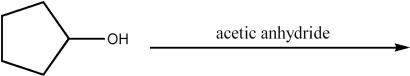
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following reagents convert(s) benzoyl chloride to phenyl propyl ketone?
A) CH3CH2CH2MgBr
B) CH3CH2CH2Li
C) (CH3CH2CH2) 2CuLi
D) both A and B
E) both A and C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
N-Methylacetamide is an example of:
A) a primary amide.
B) a secondary amide.
C) a tertiary amide.
D) an N, N-disubstituted amide.
E) an imine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Provide the major organic product in the reaction shown below. 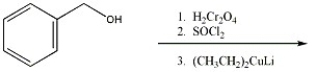
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the predicted major product of the following reaction? 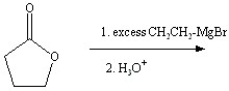
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In nucleophilic acyl substitution,
A) protonation of the carbonyl is followed immediately by loss of the leaving group.
B) loss of the leaving group is followed by rearrangement of the carbocation.
C) addition to the carbonyl by a nucleophile is followed by loss of the leaving group.
D) ester hydrolysis is followed by deprotonation.
E) an SN2 reaction occurs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Provide the major organic product in the reaction of CH3CH2CONH2 with hot aqueous acid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While the carbonyl stretching frequency for simple aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids is about 1710 cm-1, the carbonyl stretching frequency for amides is about ________.
A) 1700 cm-1
B) 1735 cm-1
C) 1800 cm-1
D) 1660 cm-1
E) 2200 cm-1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Give two different one-step methods to convert propanoic acid to methyl propanoate.
Correct Answer

verified
1. Fischer esterific...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Essay
Provide a detailed, stepwise mechanism for the reaction of 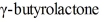 with ammonia.
with ammonia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Acids can be reduced to aldehydes by:
A) treatment with LiAlH4.
B) conversion to the acid chloride followed by treatment with LiAlH[OC(CH3) 3]3.
C) conversion to the amide followed by treatment with NaBH4.
D) conversion to the ester followed by treatment with LiAlH4.
E) conversion to the anhydride followed by treatment with Mg and H3O+.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Propose a synthesis of benzonitrile from benzene and any other necessary reagents.
Correct Answer

verified
1. HNO3, H2S...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Essay
What reagents are used to dehydrate amides to nitriles?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 128
Related Exams